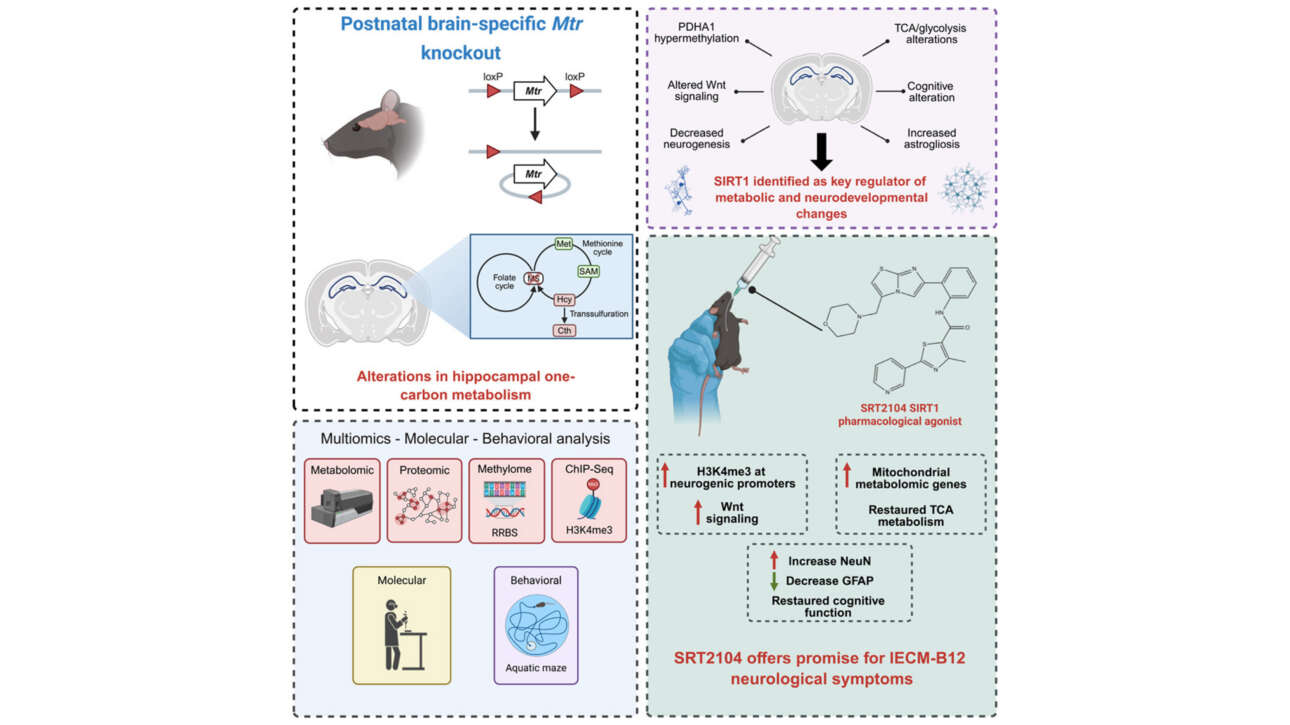
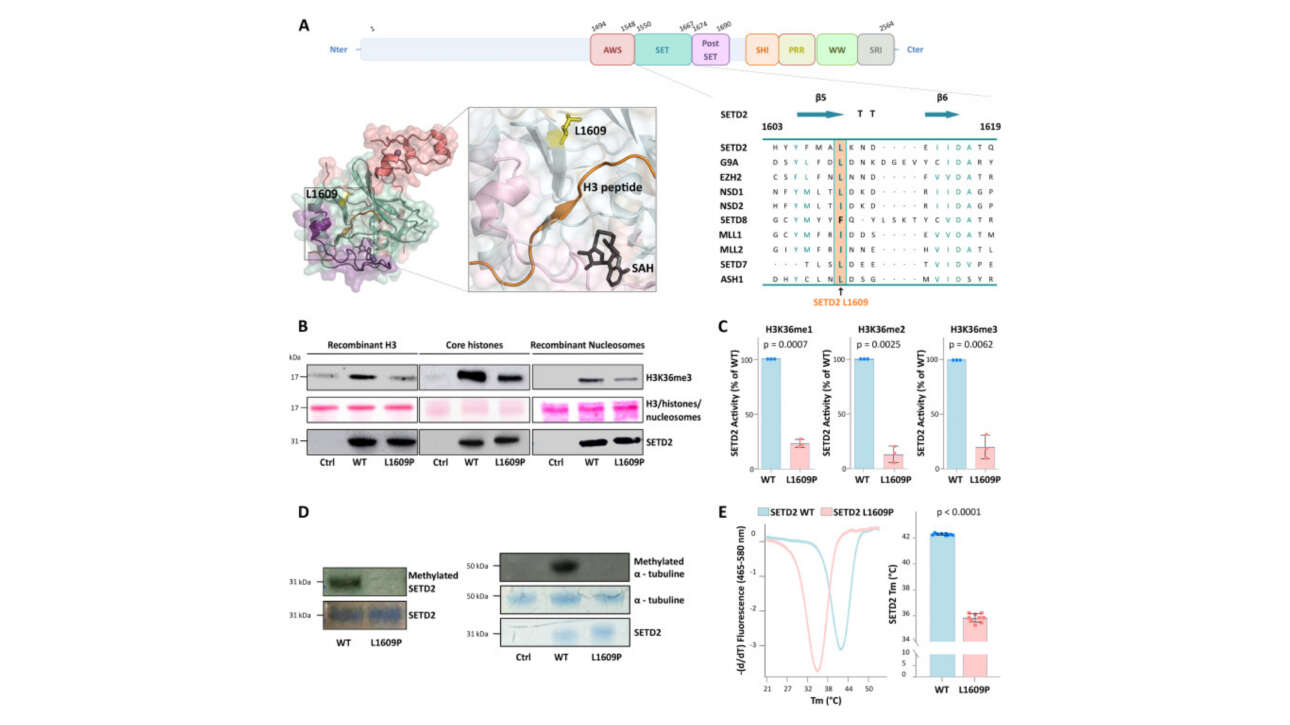
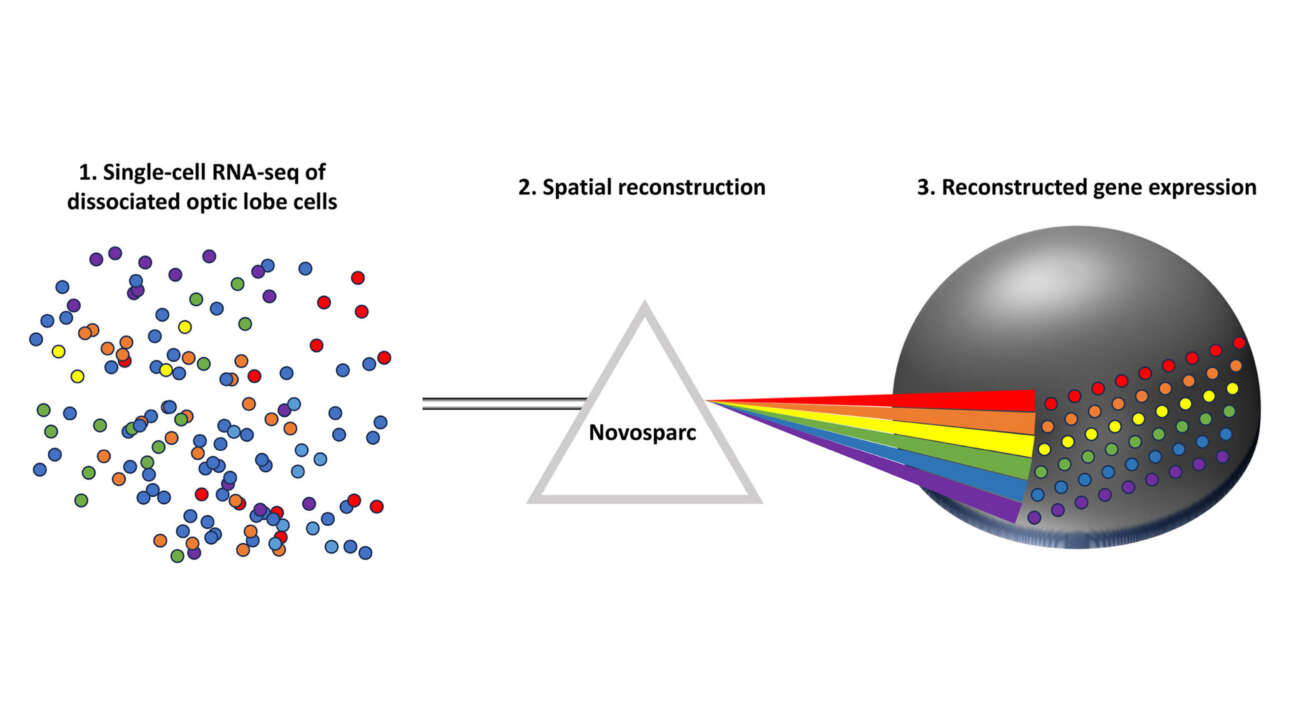
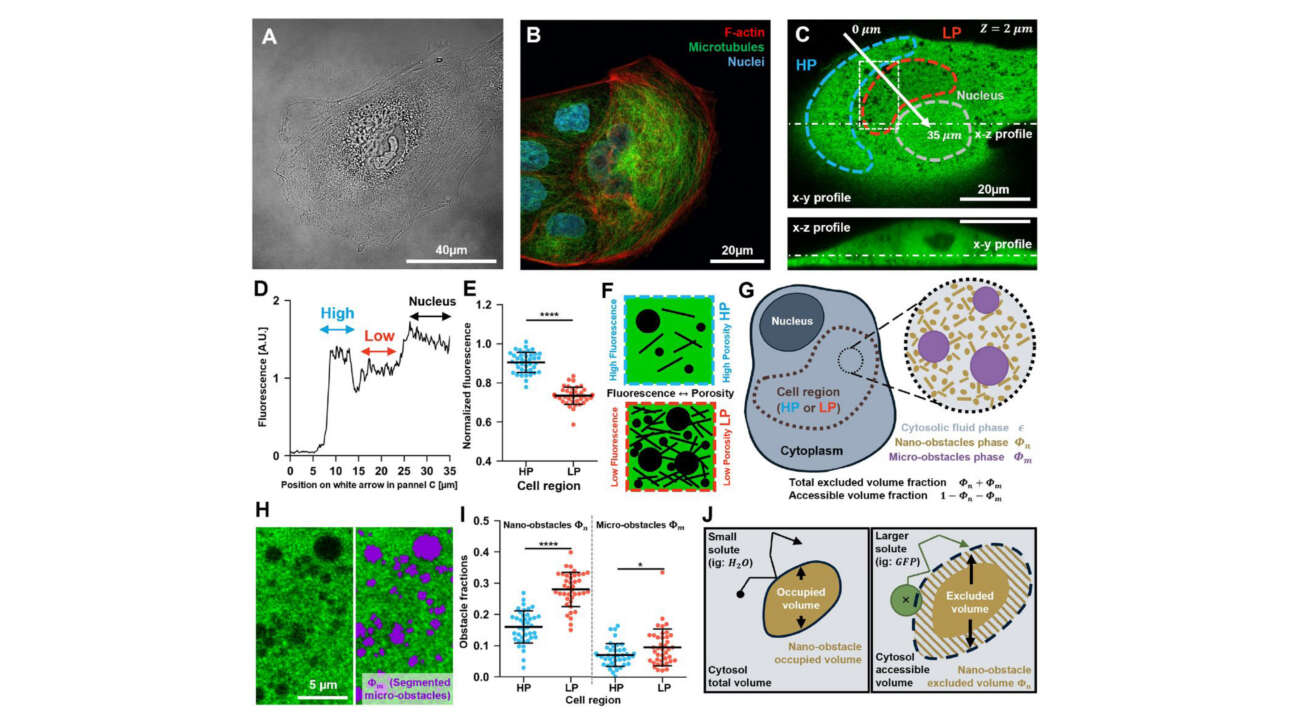
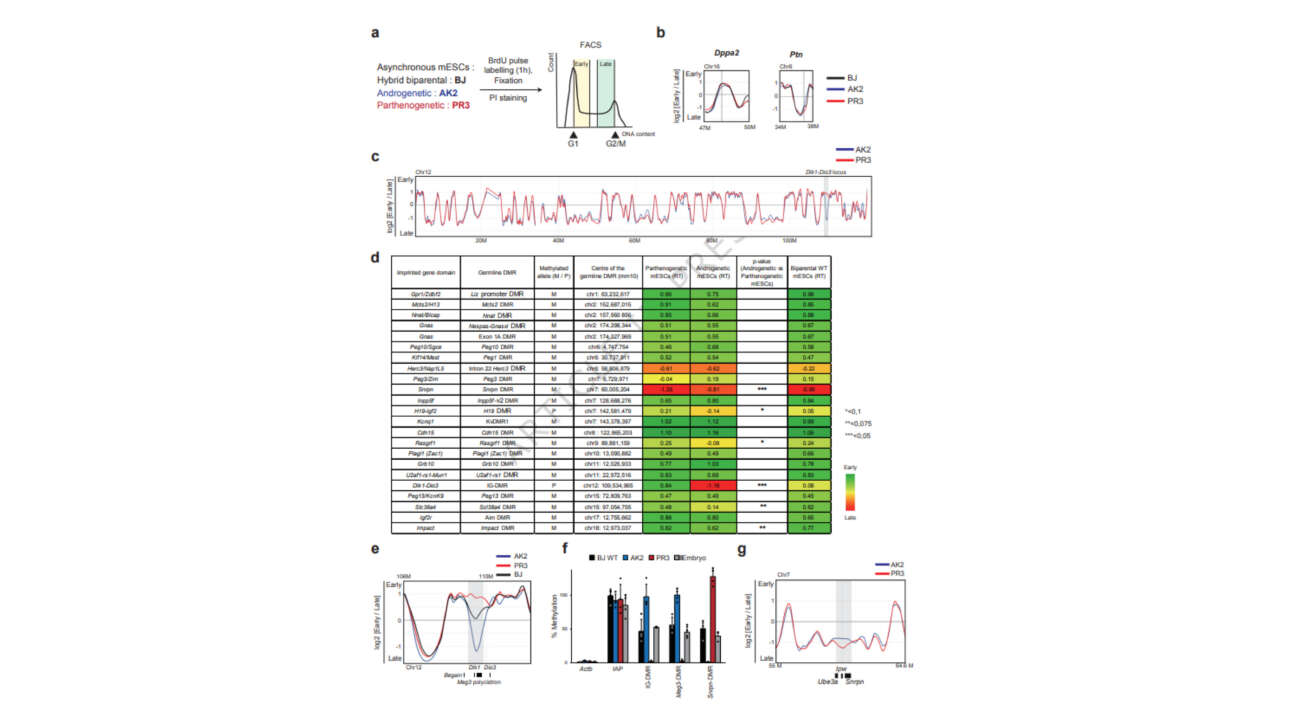
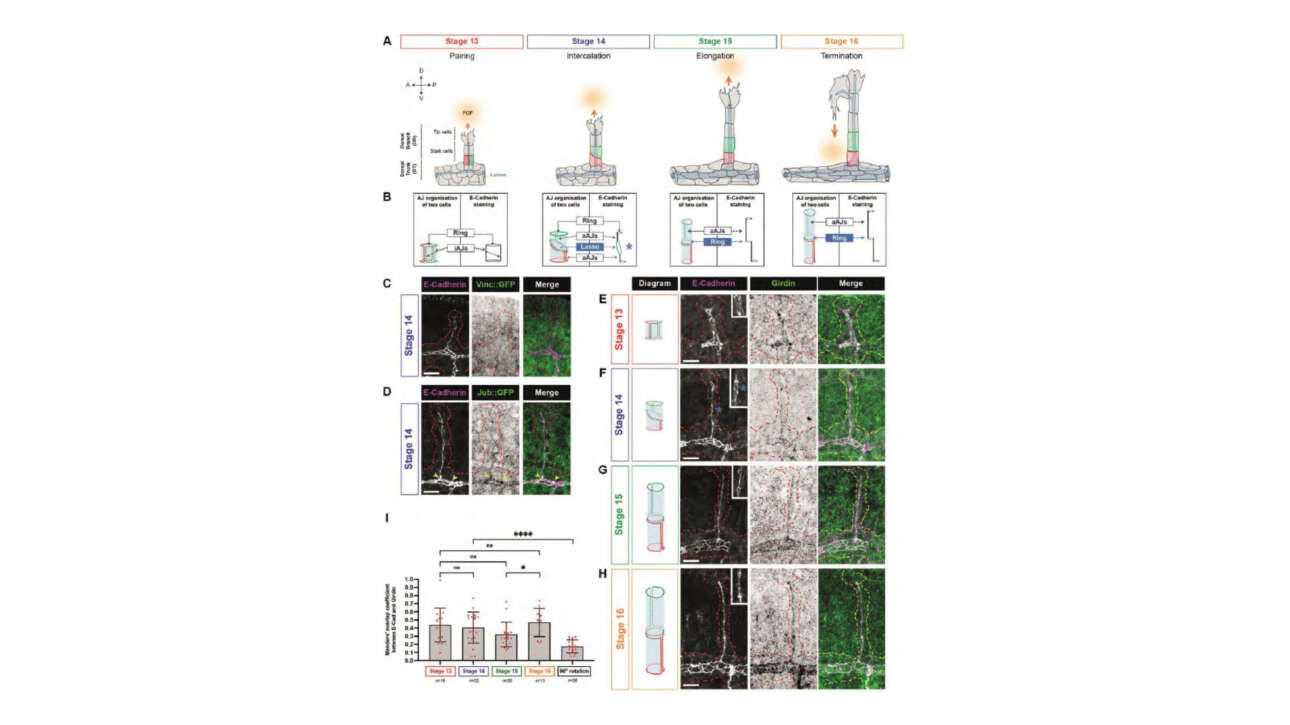
L'ancienne équipe Camadro et la plateforme ProtéoSeine ont contribué à la publication d'un nouvel article dans Cell Reports Medicine :
SIRT1 mediates brain metabolic and developmental consequences of methionine synthase deficiency in inborn errors of cobalamin metabolism
Résumé :
Inborn errors of vitamin B12 metabolism (IECM) resulting from impaired methionine synthase (MTR) activity cause severe cognitive and…