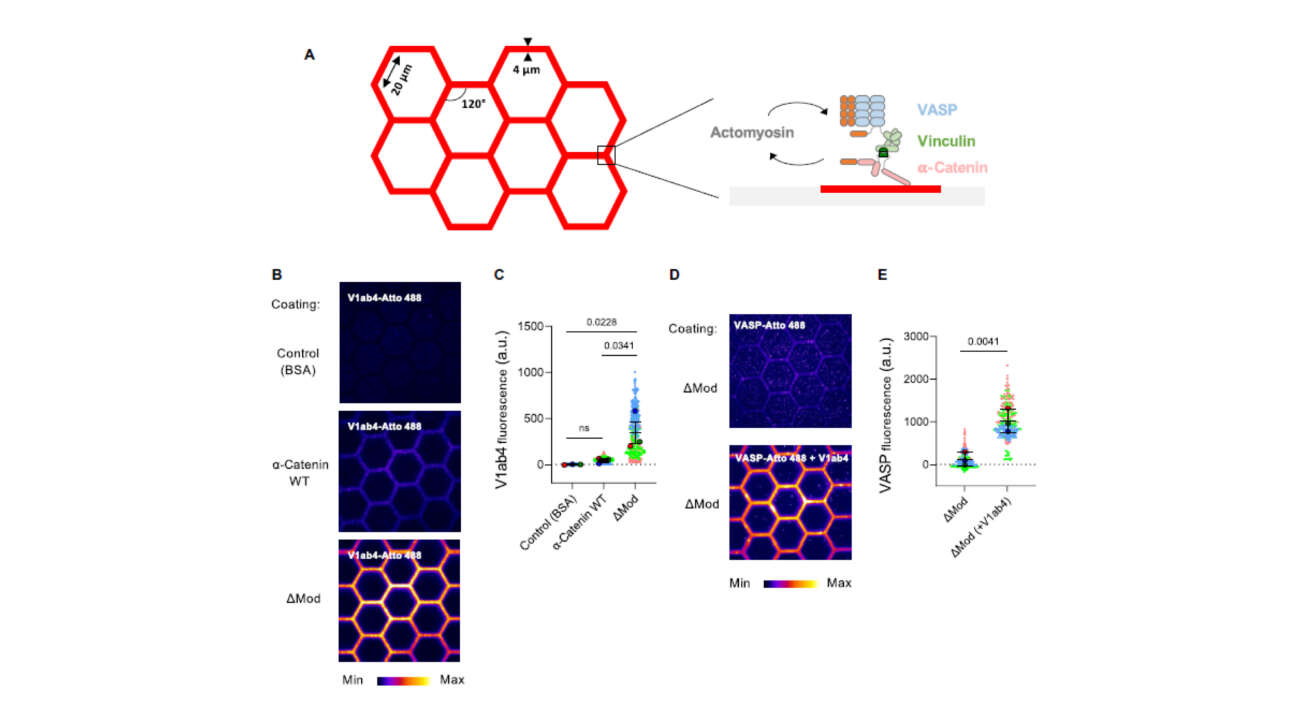
L'équipe Ladoux-Mège a contribué à la publication d'un nouvel article dans Science advances :
Actomyosin-dependent assembly of the mechanosensitive machinery from adherens junctions triggers actin polymerization and organization
Résumé :
Cells rely on cadherin-based adherens junctions (AJs) to form cohesive tissues. To establish contact, cells generate pushing forces through branched actin polymerization mediated by the actin-related protein…