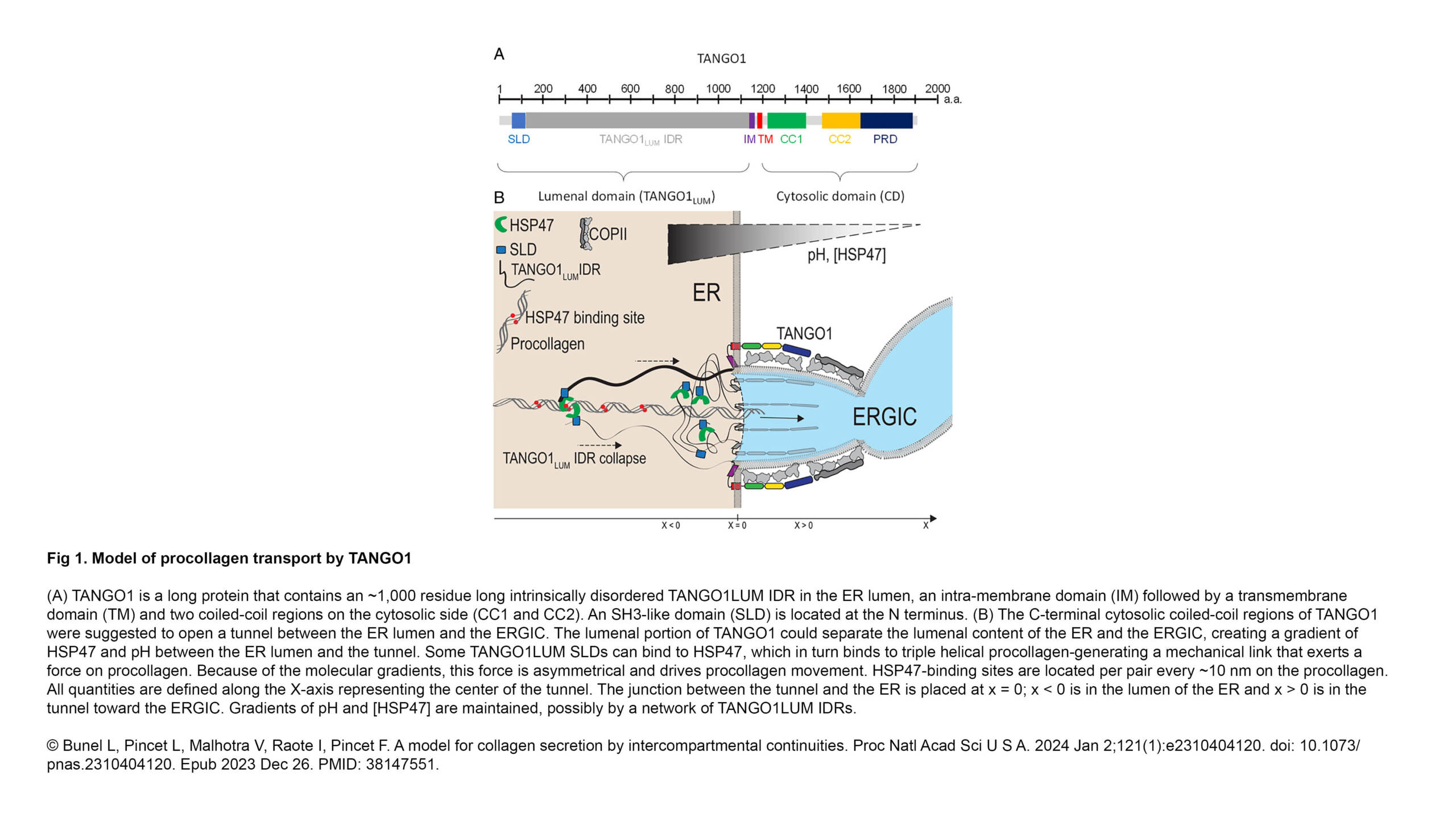
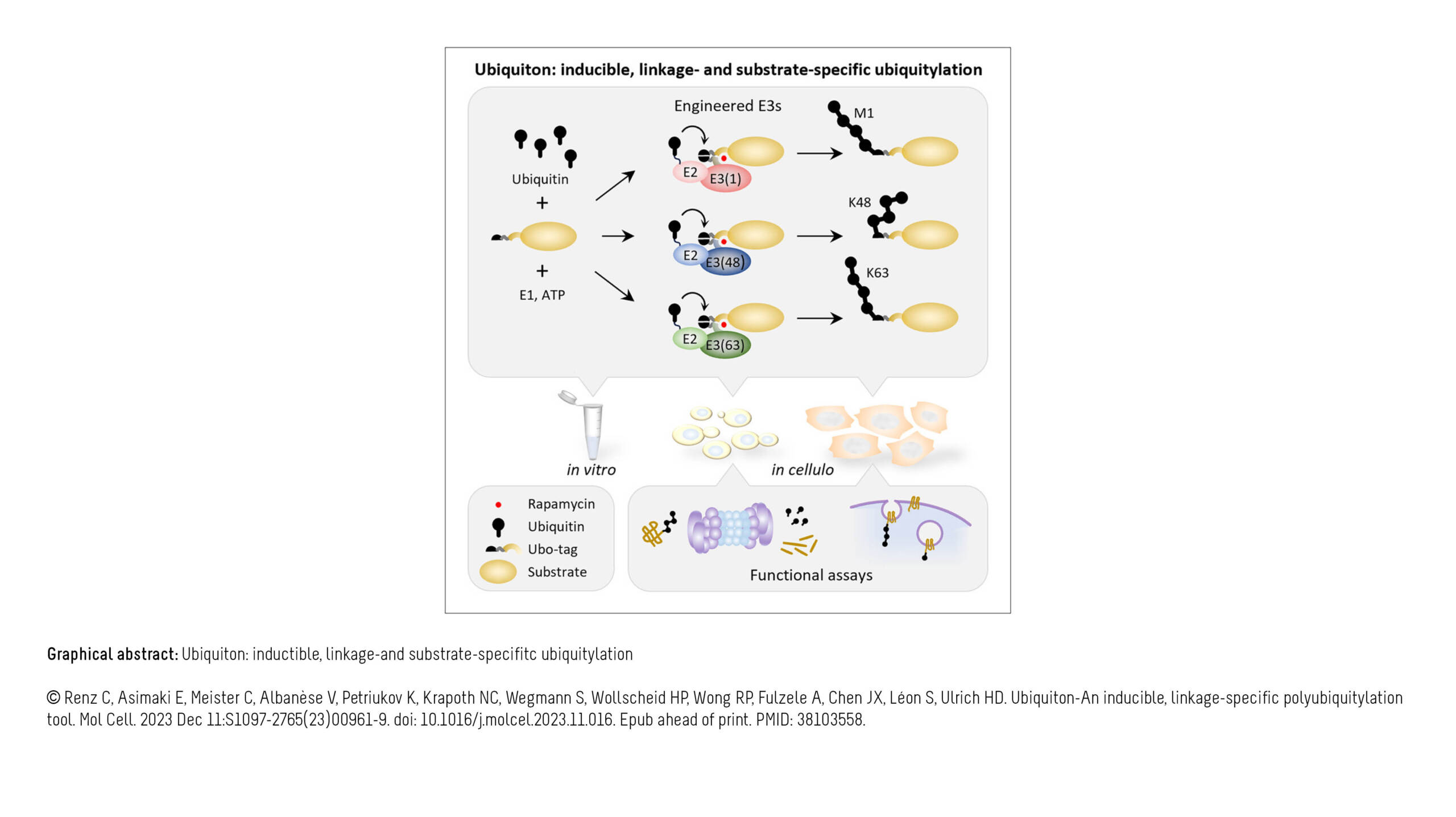
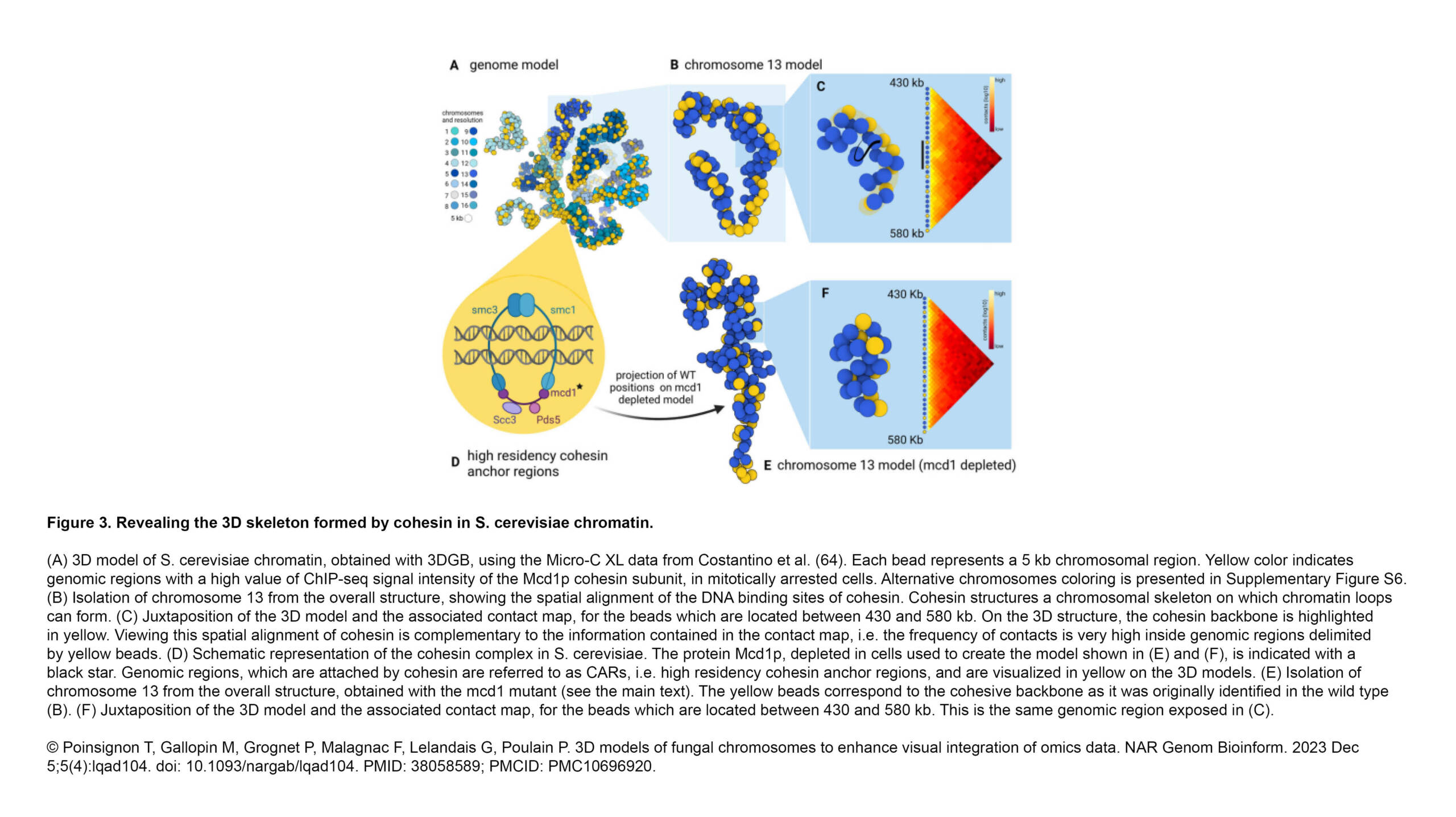
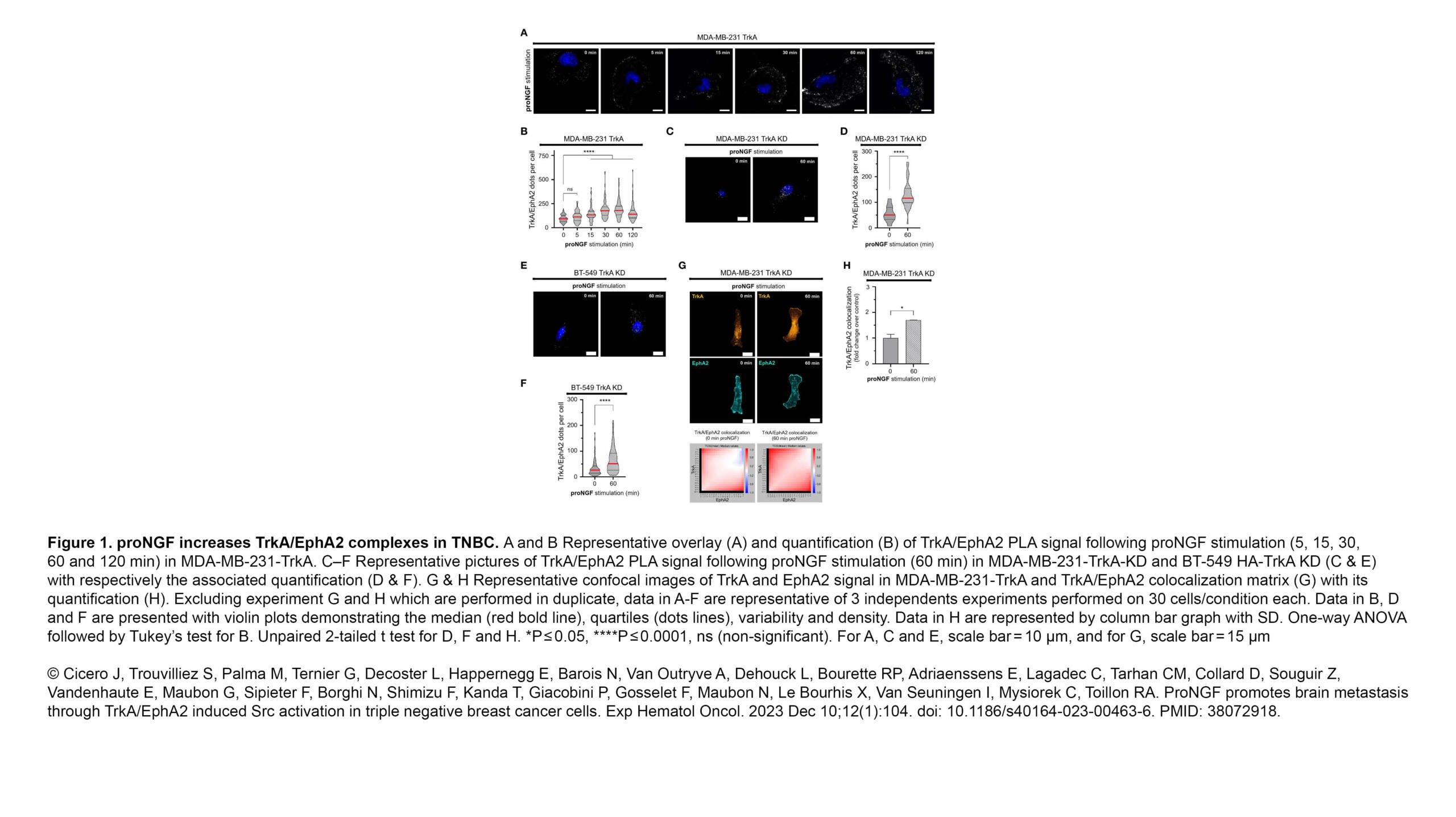
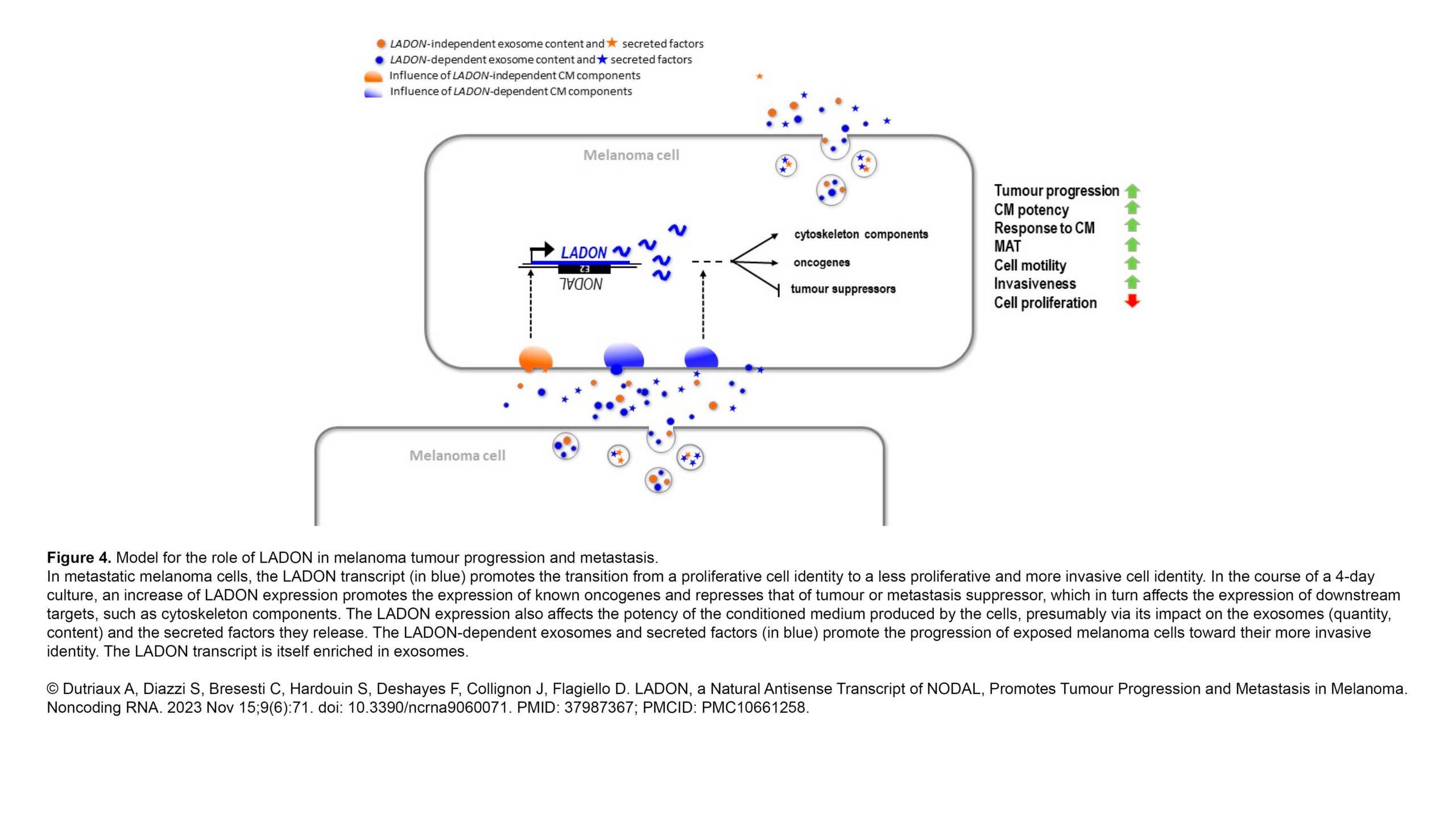
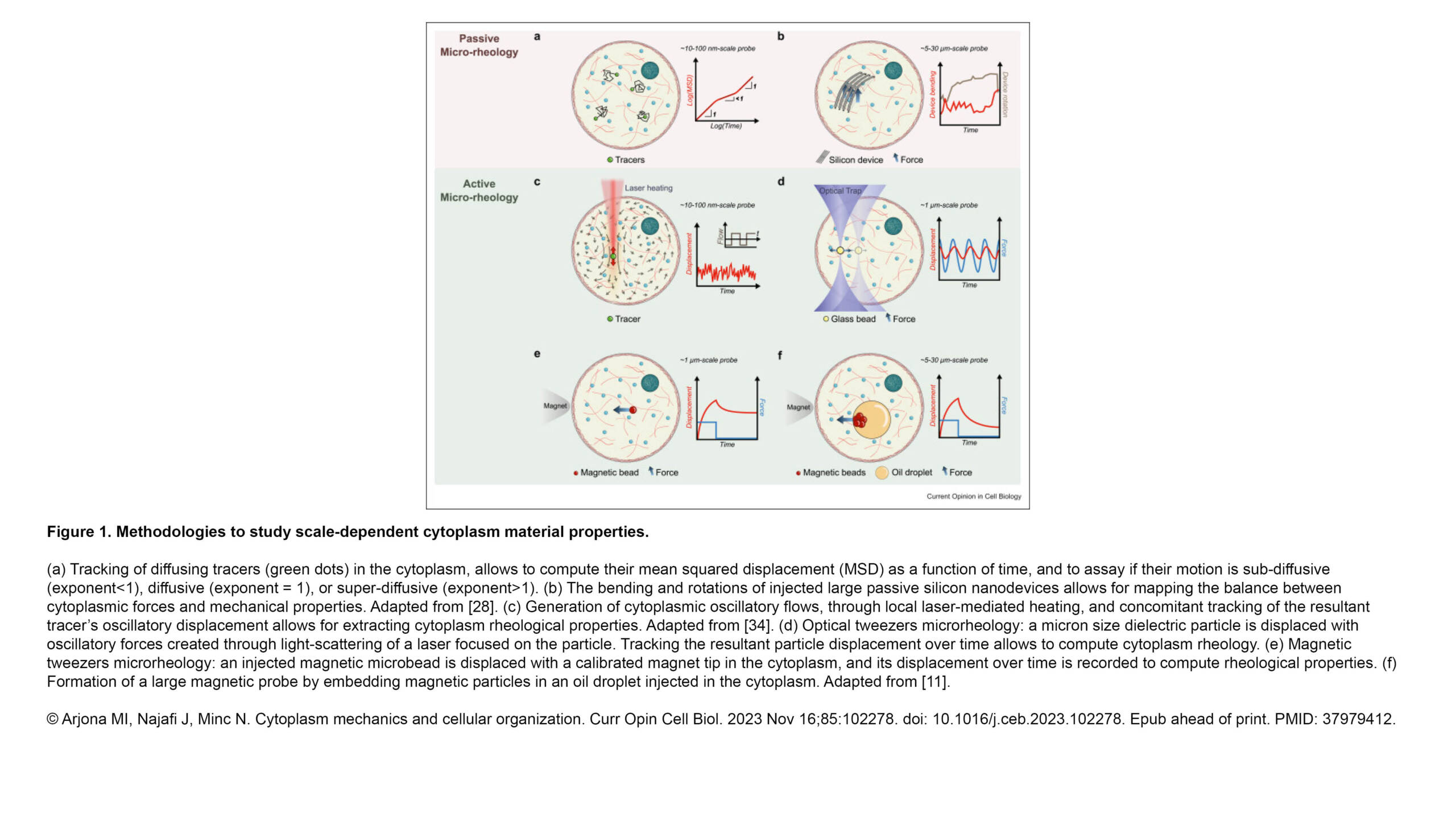
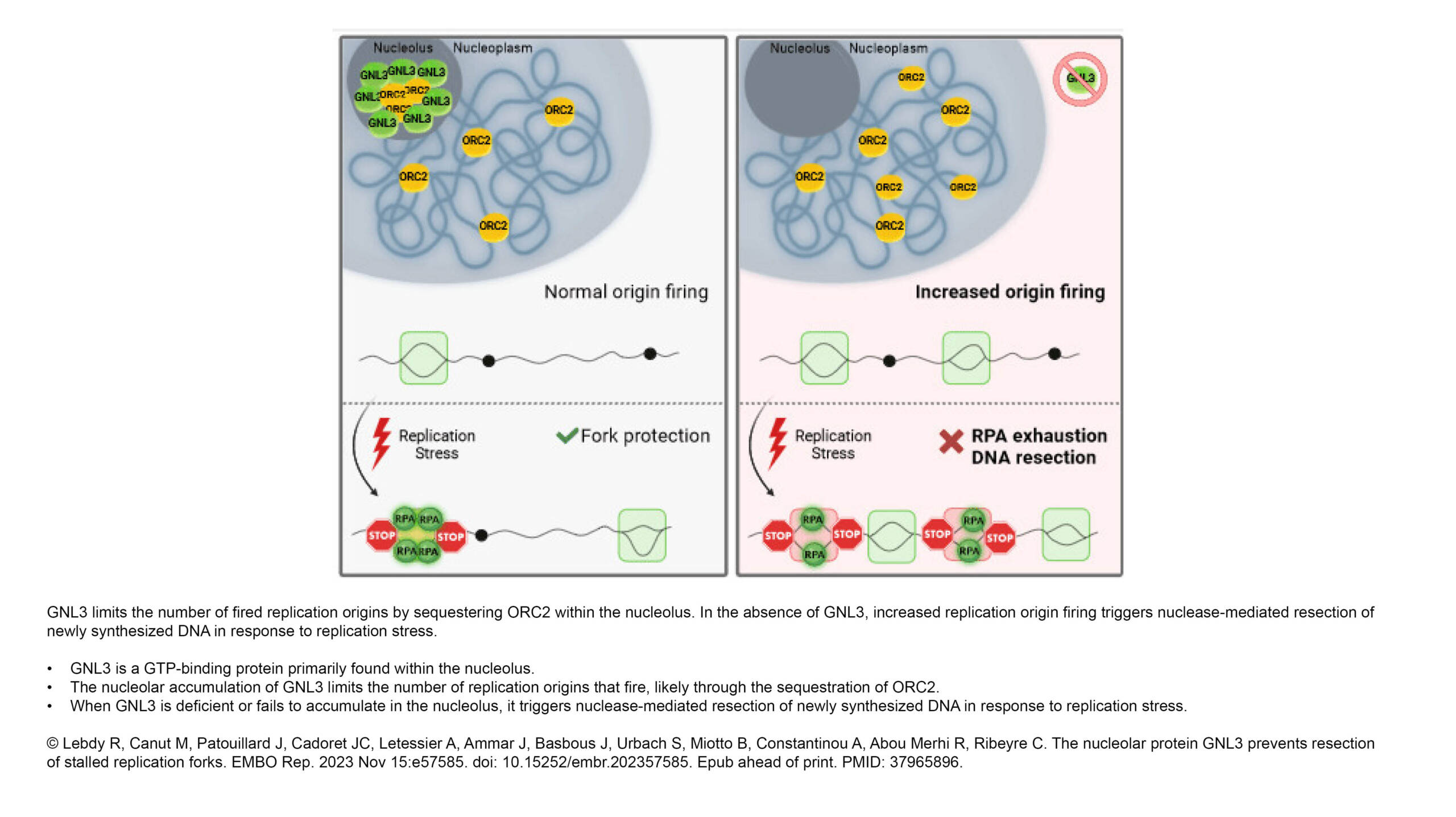
L'équipe Raote a contribué à la publication d'un nouvel article dans PNAS :
A model for collagen secretion by intercompartmental continuities
Résumé : Newly synthesized secretory proteins are exported from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) at specialized subcompartments called exit sites (ERES). Cargoes like procollagen are too large for export by the standard COPII-coated vesicle of 60 nm…