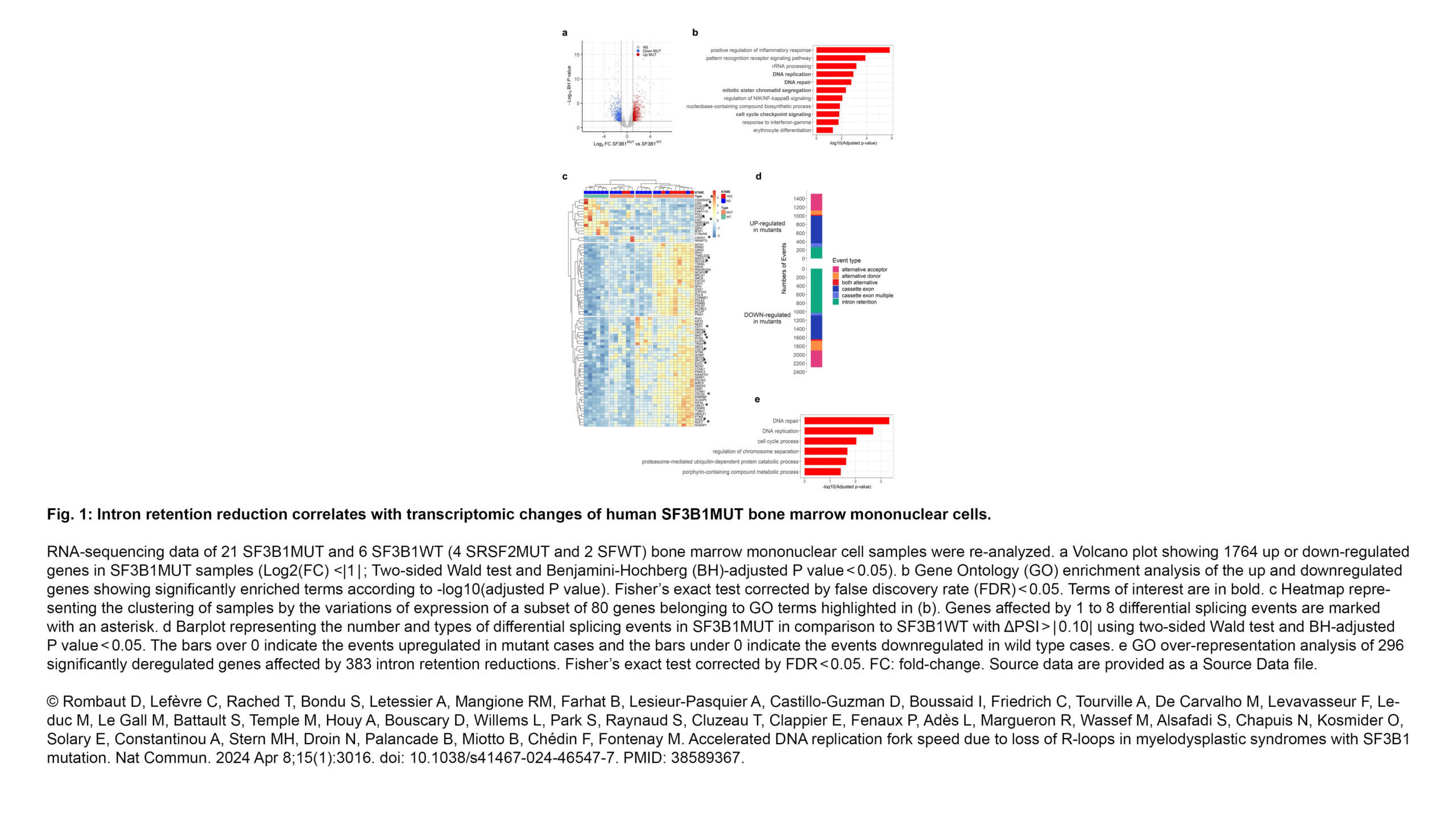
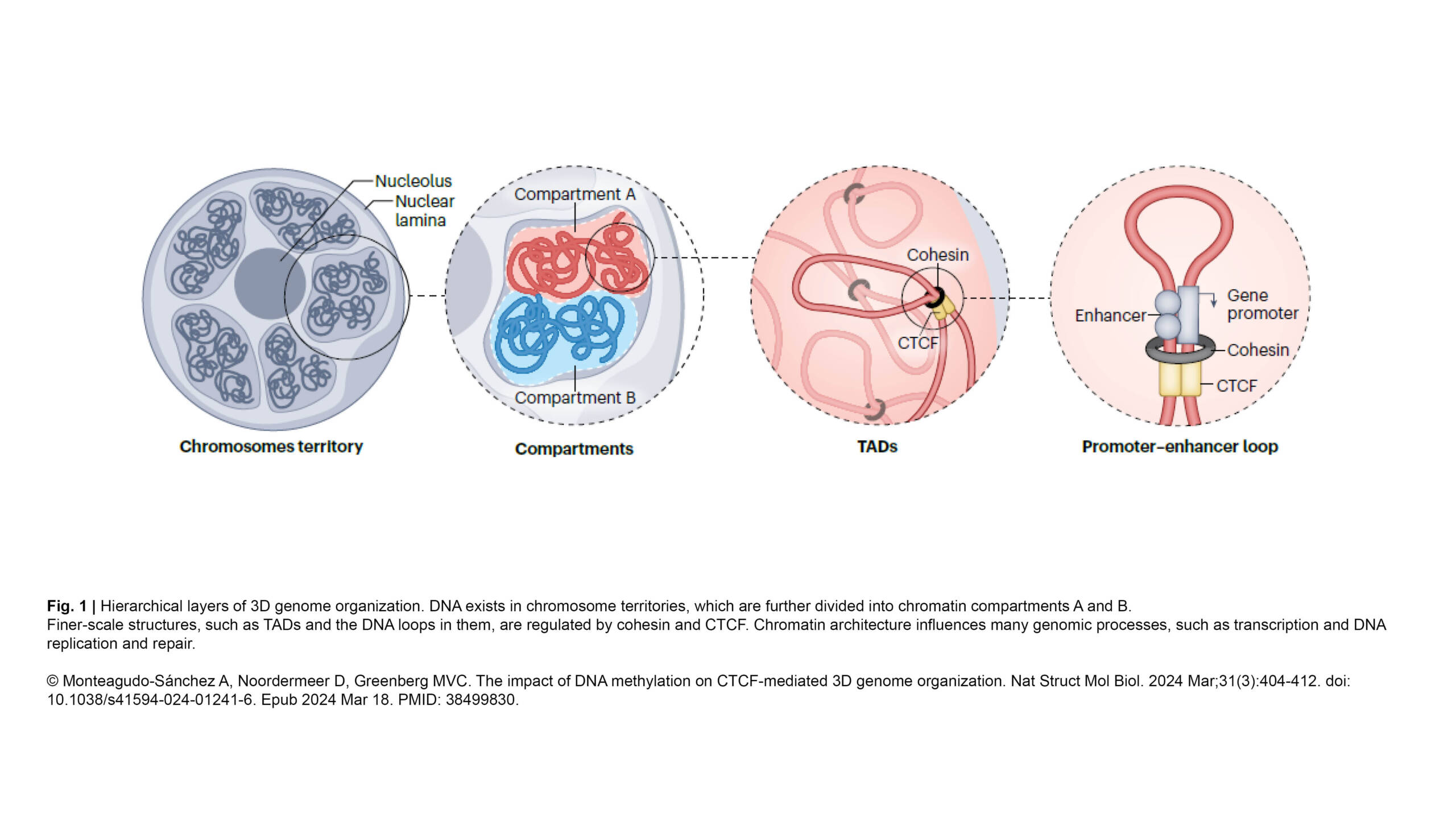
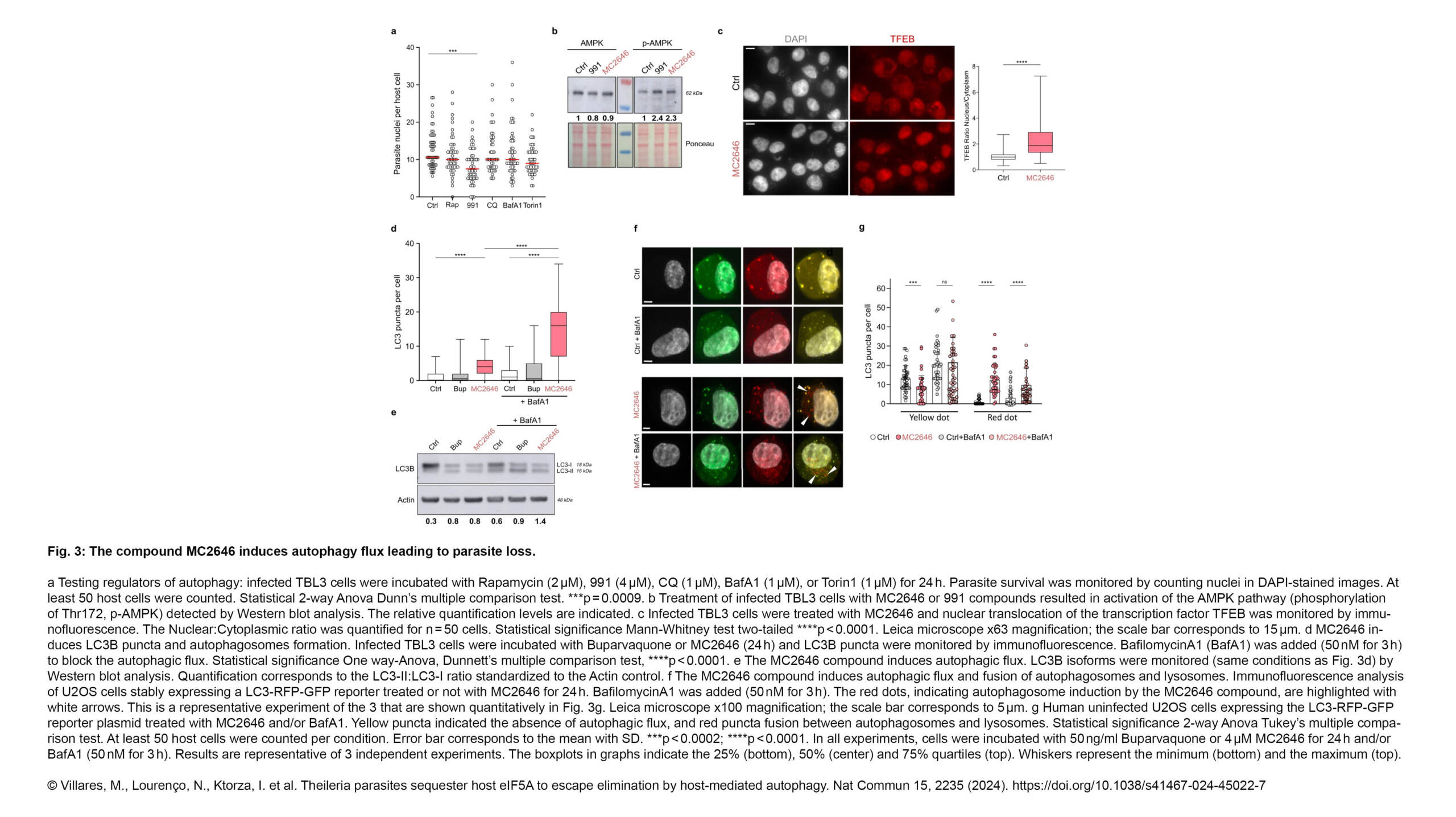
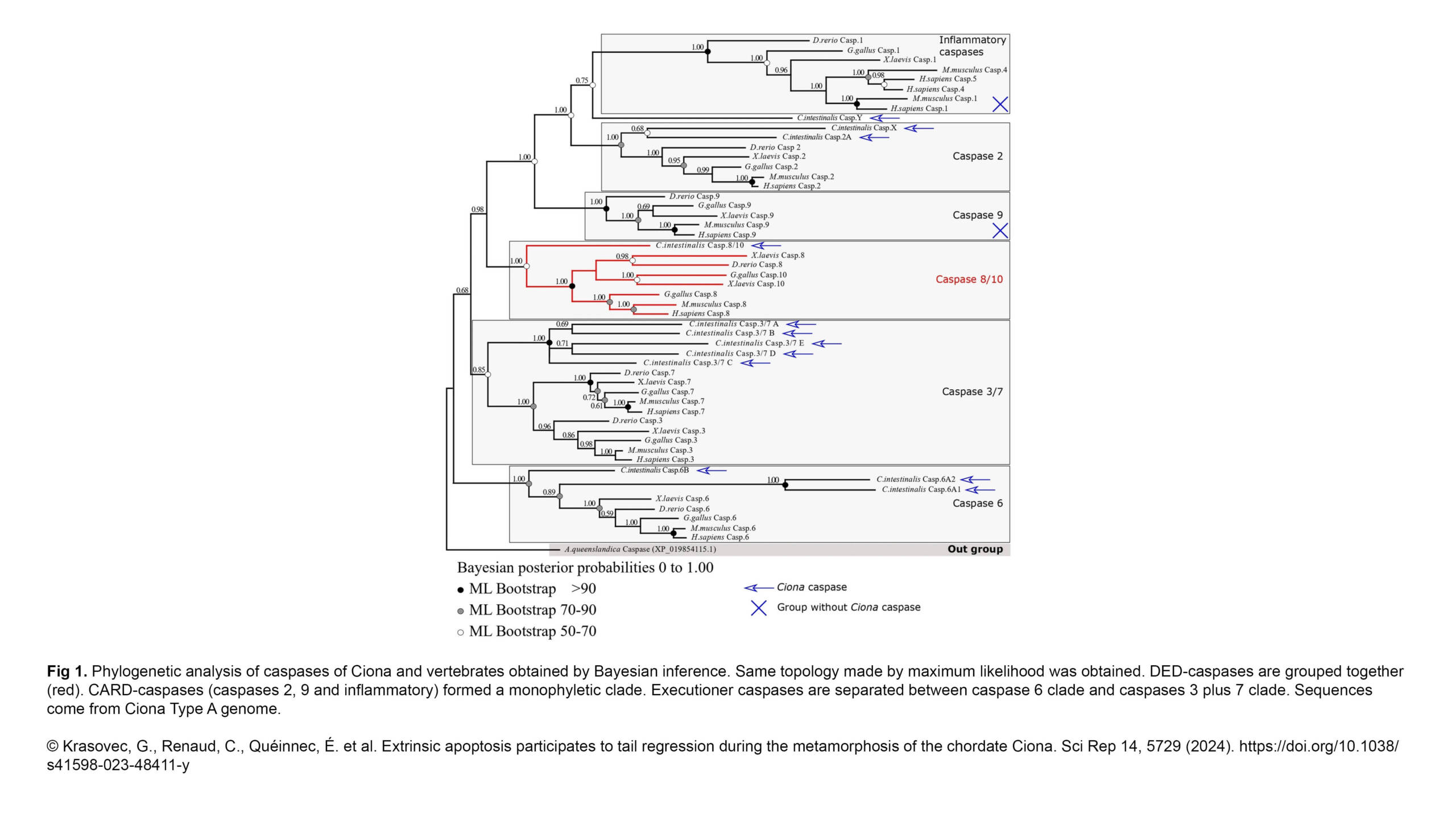
L'équipe Conduit a publié un nouvel article dans Journal of Cell Science :
γ-TuRCs and Augmin are required for the development of highly branched dendritic arbors in Drosophila
Résumé :
Microtubules are nucleated by γ-tubulin ring complexes (γ-TuRCs) and are essential for neuronal development. Nevertheless, γ-TuRC depletion has been reported to perturb only higher-order branching in elaborated Drosophila larval…