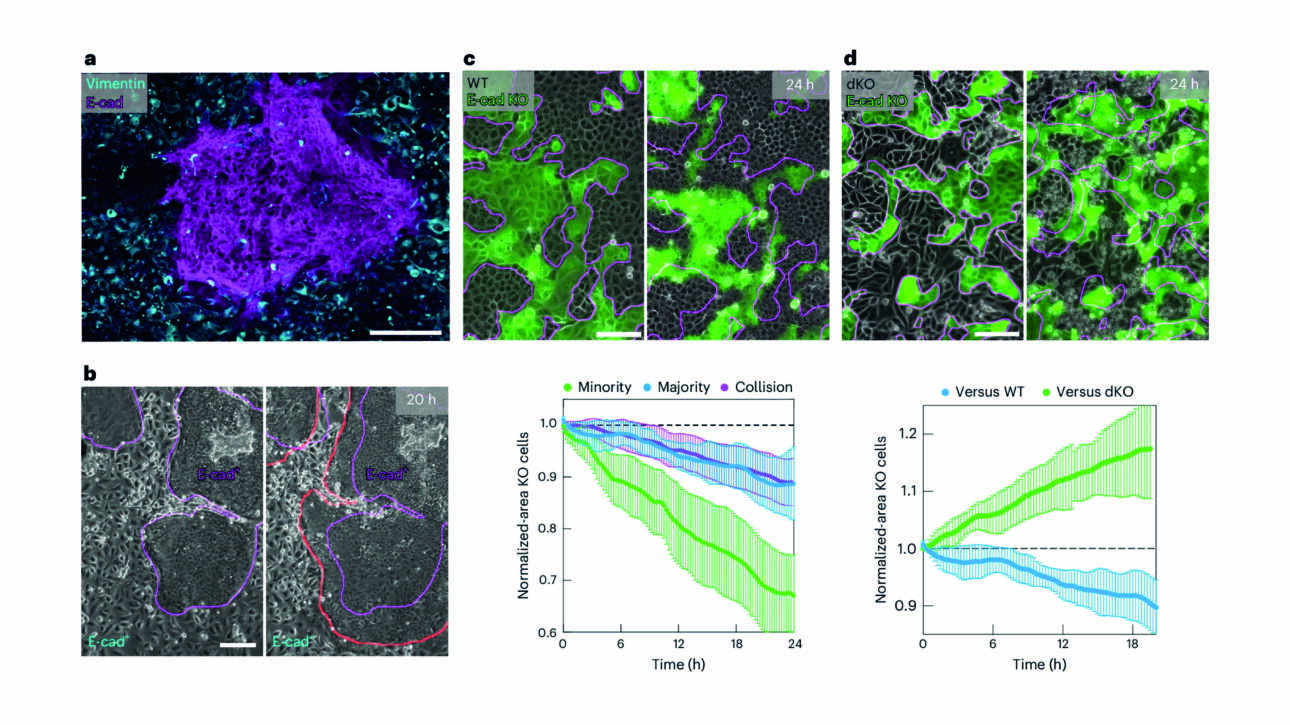
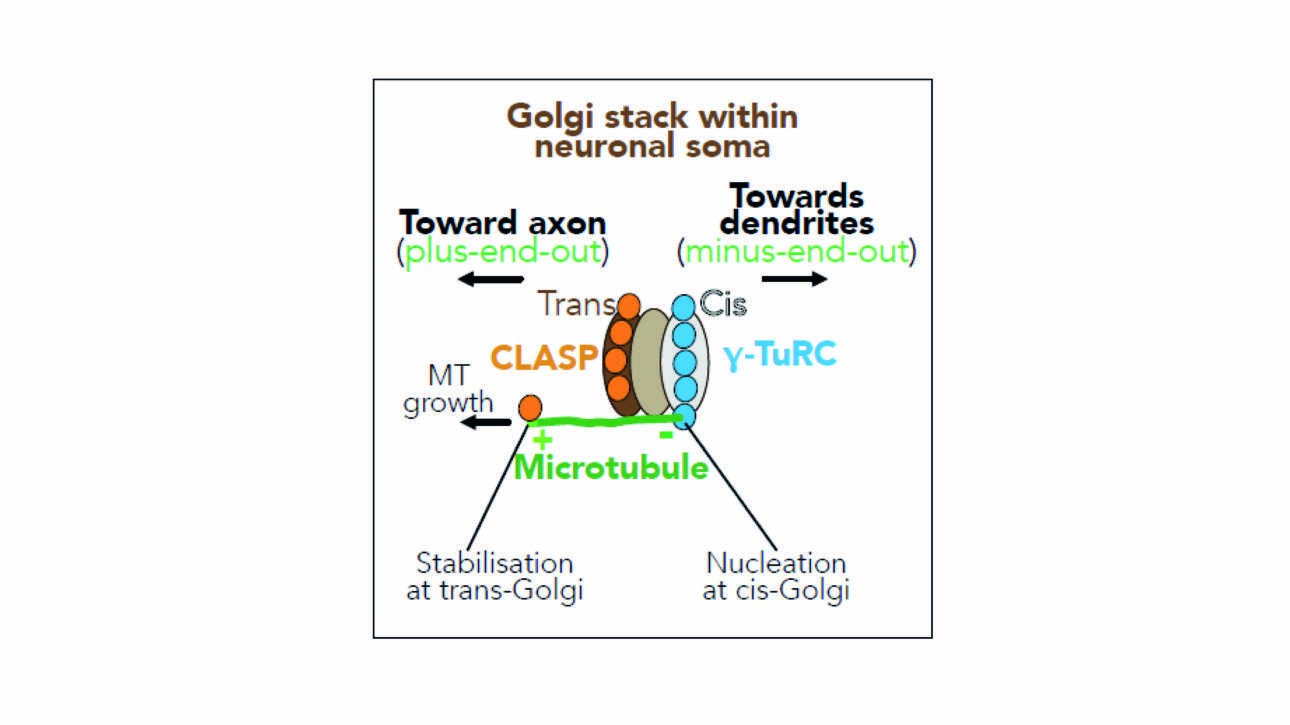
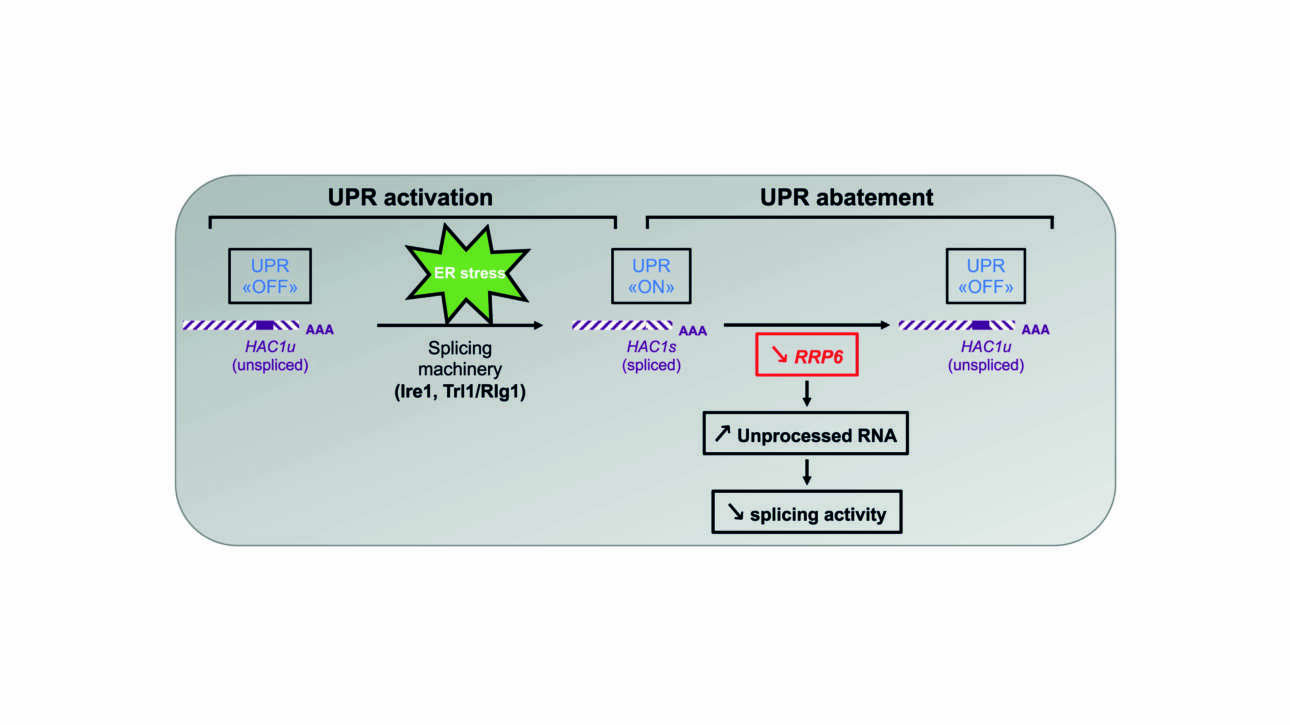
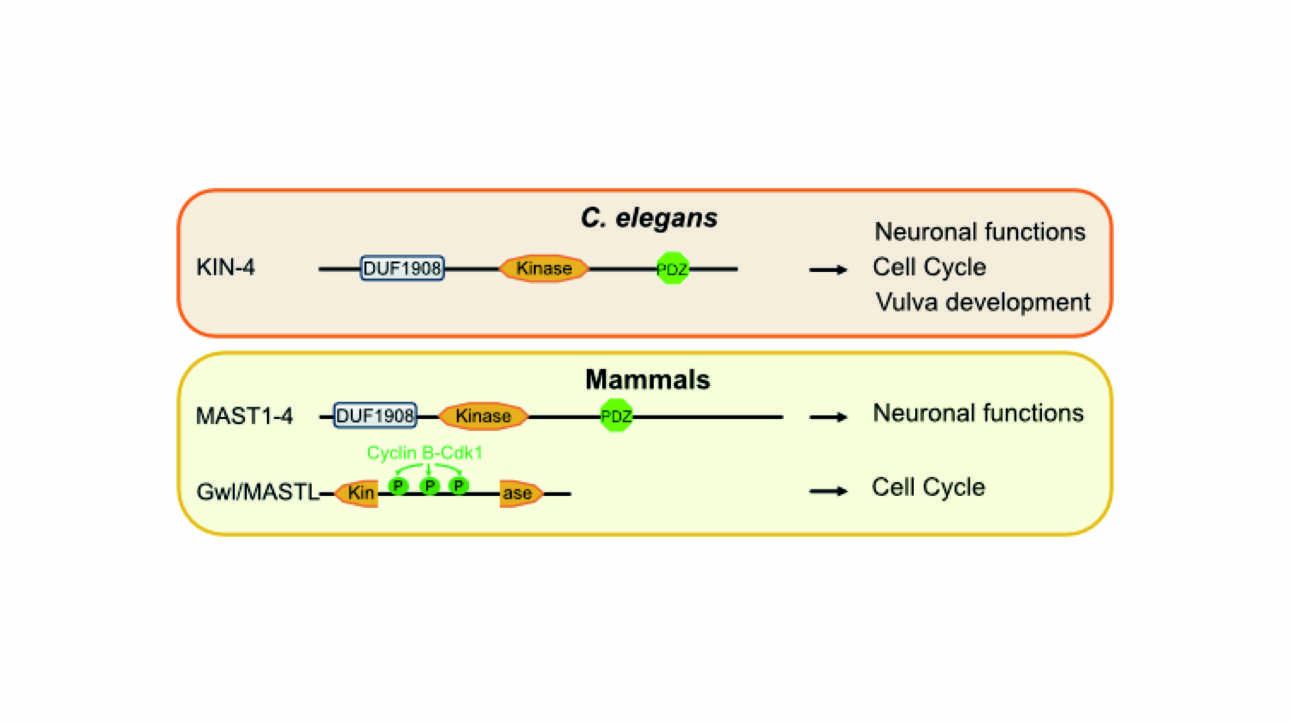
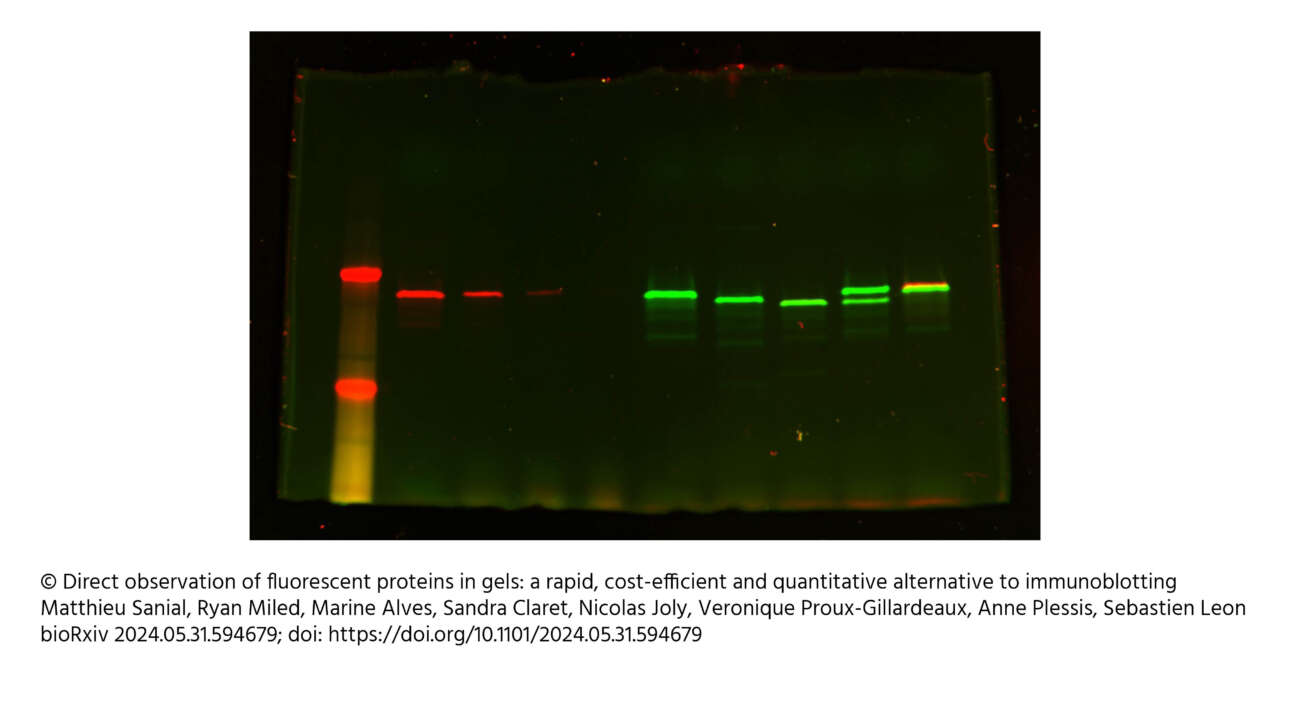
The Ladoux/Mège published a new article in Nature material:
Force transmission is a master regulator of mechanical cell competition
Abstract:
Cell competition is a tissue surveillance mechanism for eliminating unwanted cells, being indispensable in development, infection and tumourigenesis. Although studies have established the role of biochemical mechanisms in this process, due to challenges in measuring forces in…