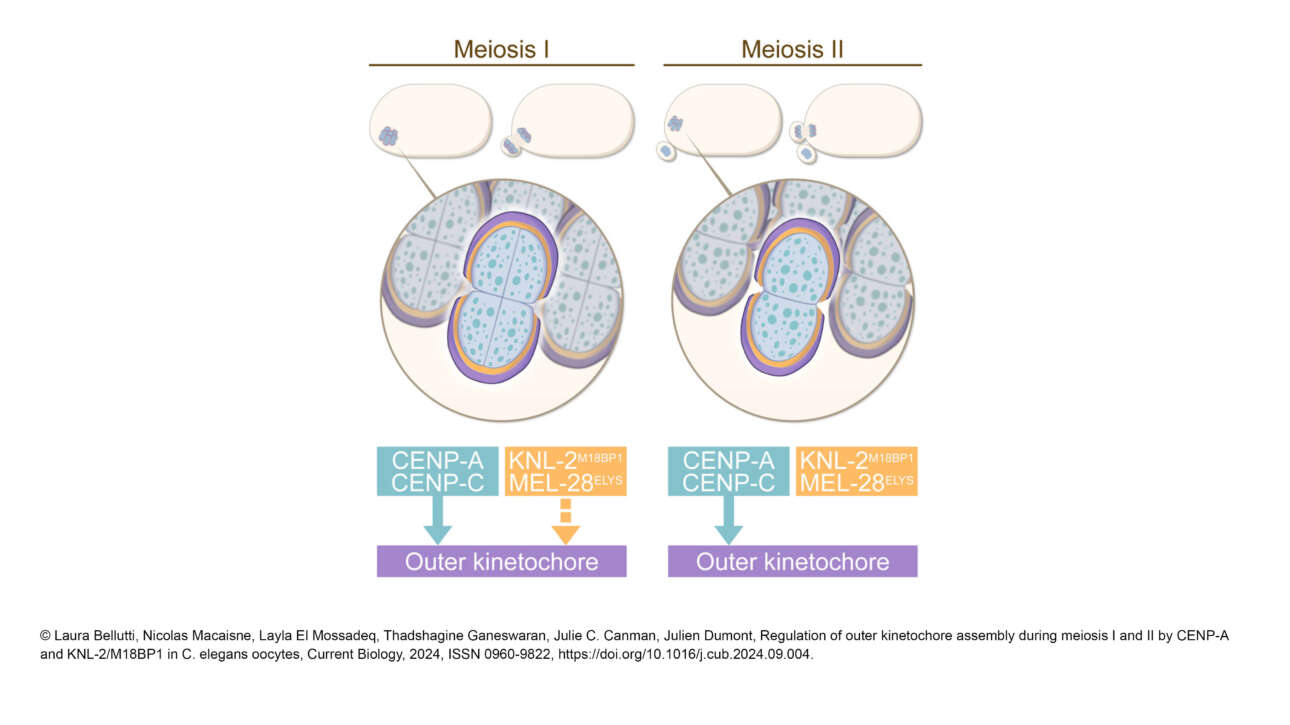
The Dumont Lab published a new article in Current Biology :
Regulation of outer kinetochore assembly during meiosis I and II by CENP-A and KNL-2/M18BP1 in C. elegans oocytes
Abstract:
During cell division, chromosomes build kinetochores that attach to spindle microtubules. Kinetochores usually form at the centromeres, which contain CENP-A nucleosomes. The outer kinetochore, which is the core attachment…