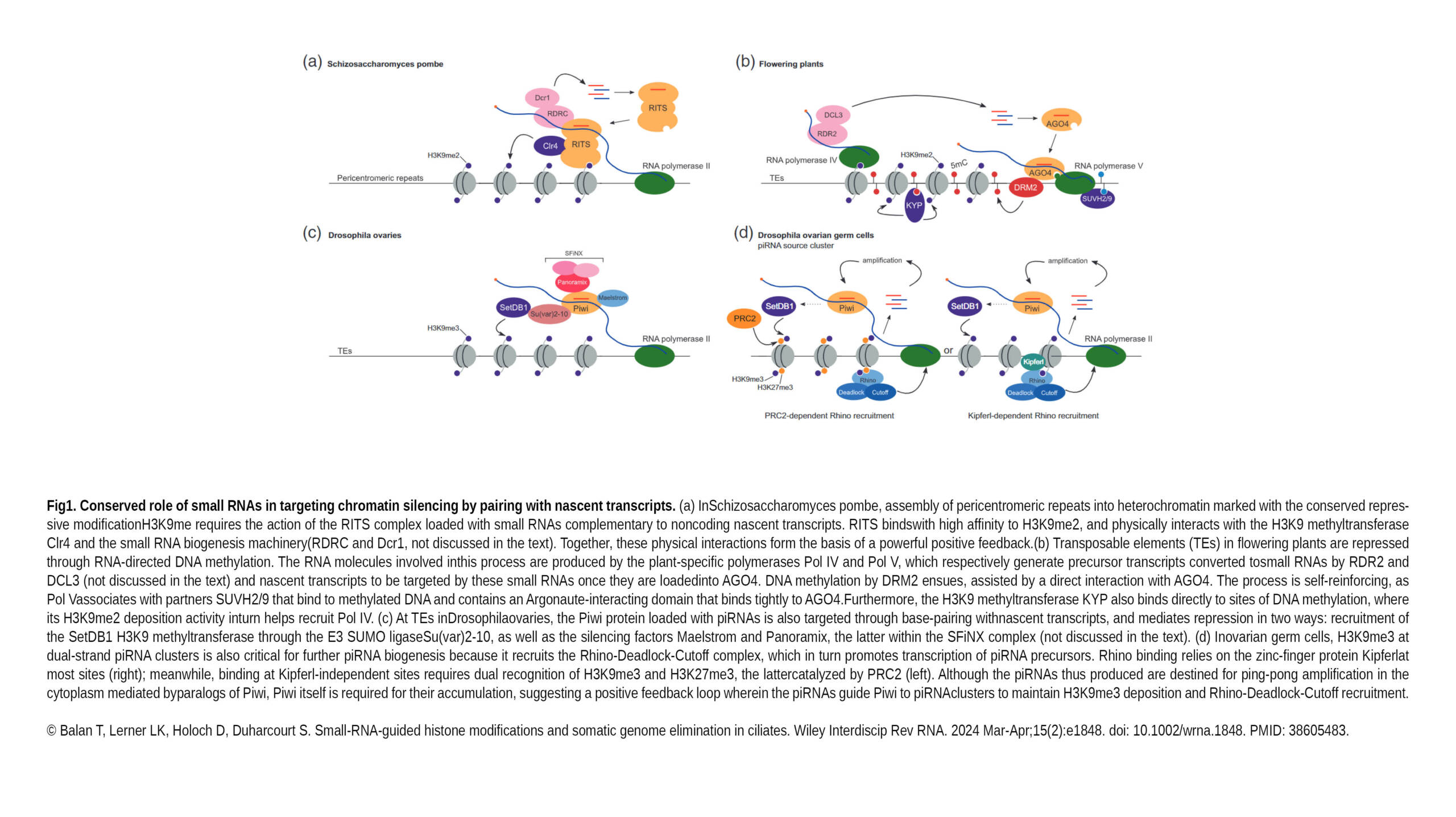
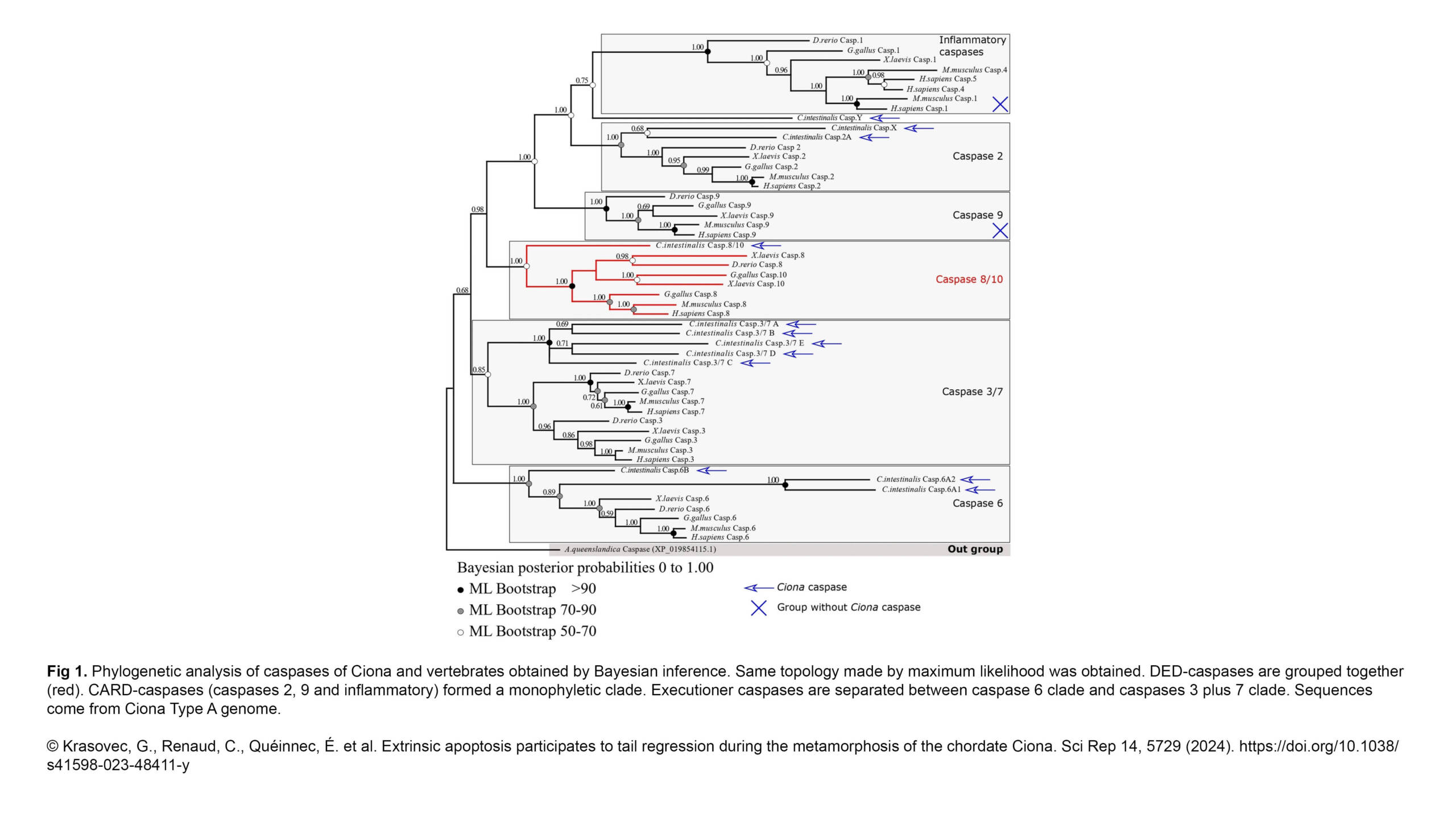
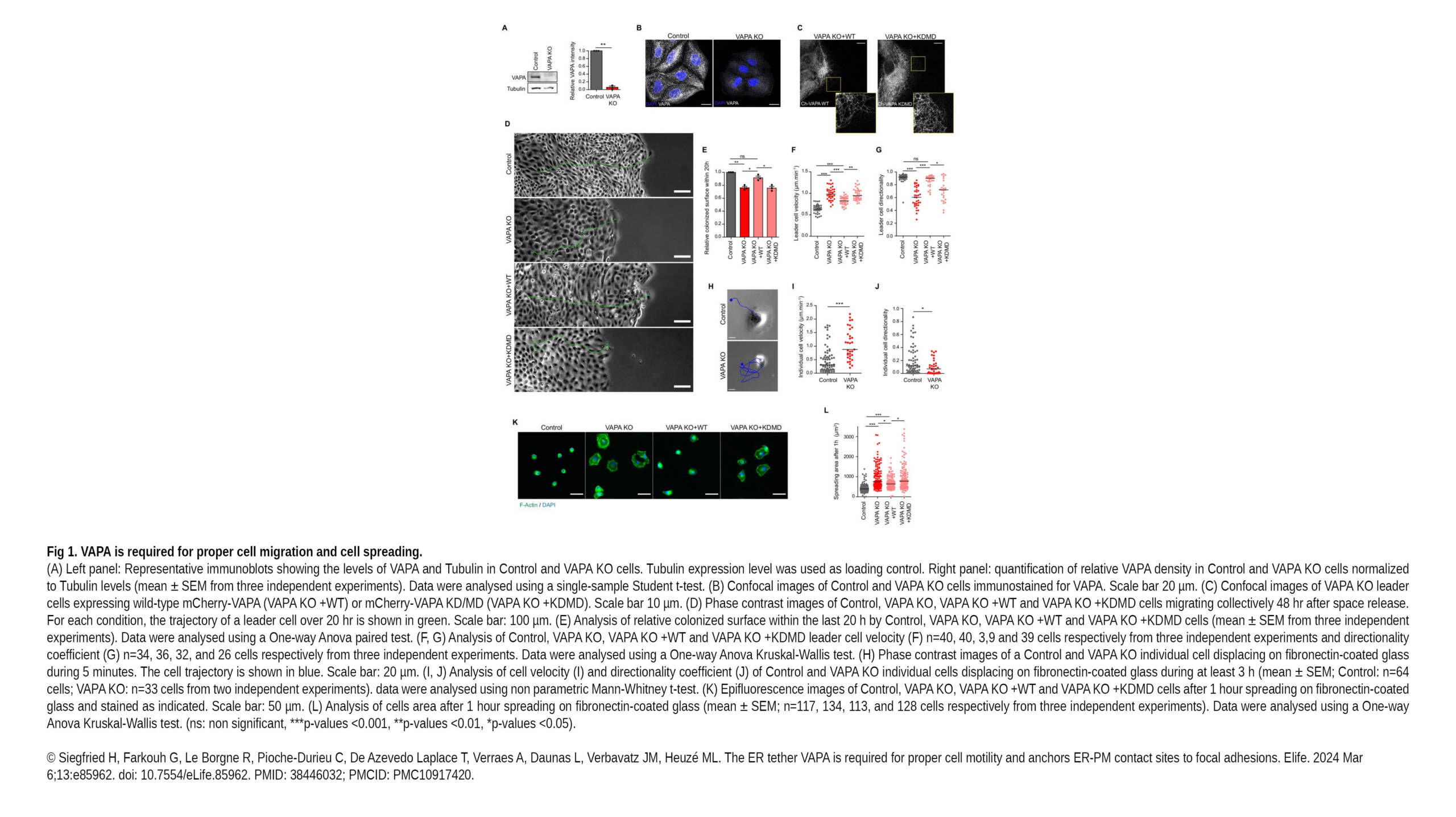
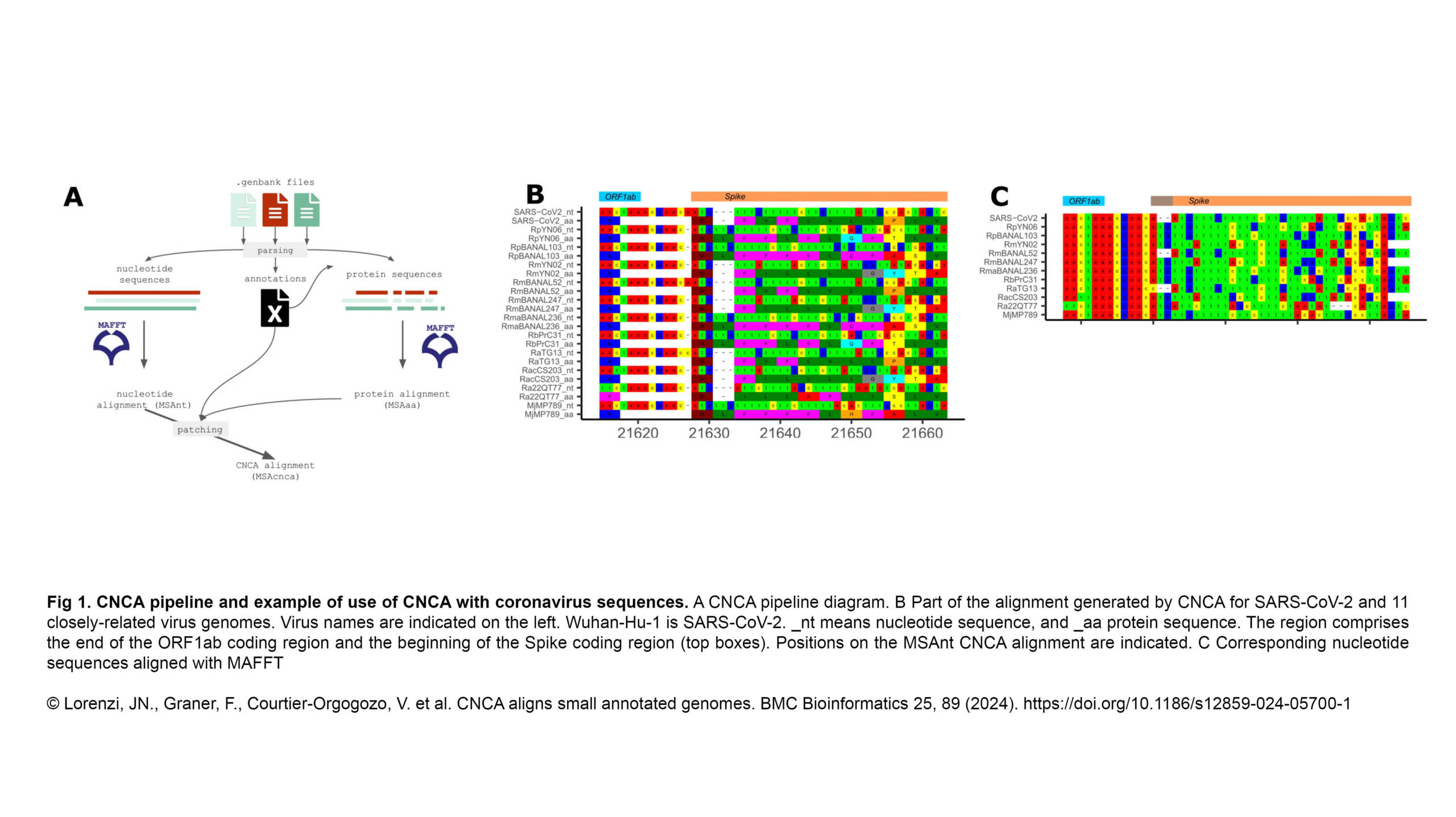
The Duharcourt Lab published a new review in WIREs RNA :
Small-RNA-guided histone modifications and somatic genome elimination in ciliates
Abstract:
Transposable elements and other repeats are repressed by small-RNA-guided histone modifications in fungi, plants and animals. The specificity of silencing is achieved through base-pairing of small RNAs corresponding to the these genomic loci to nascent noncoding…