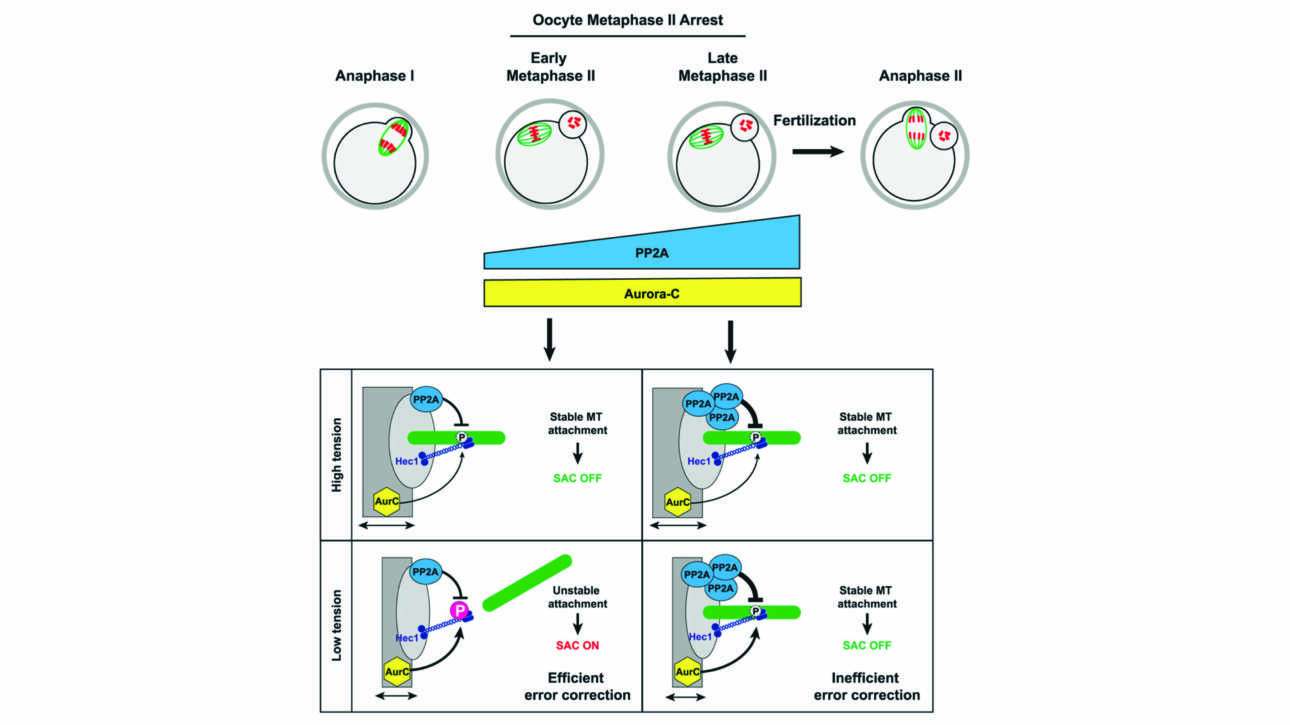
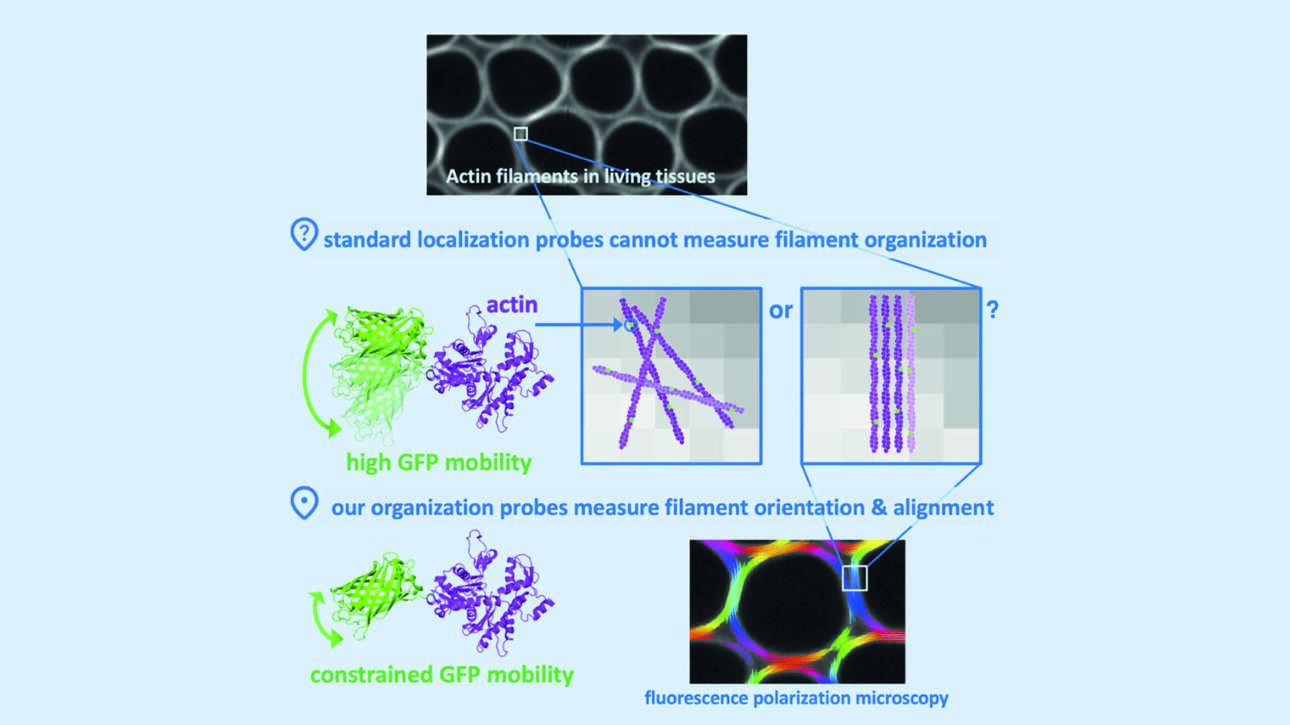
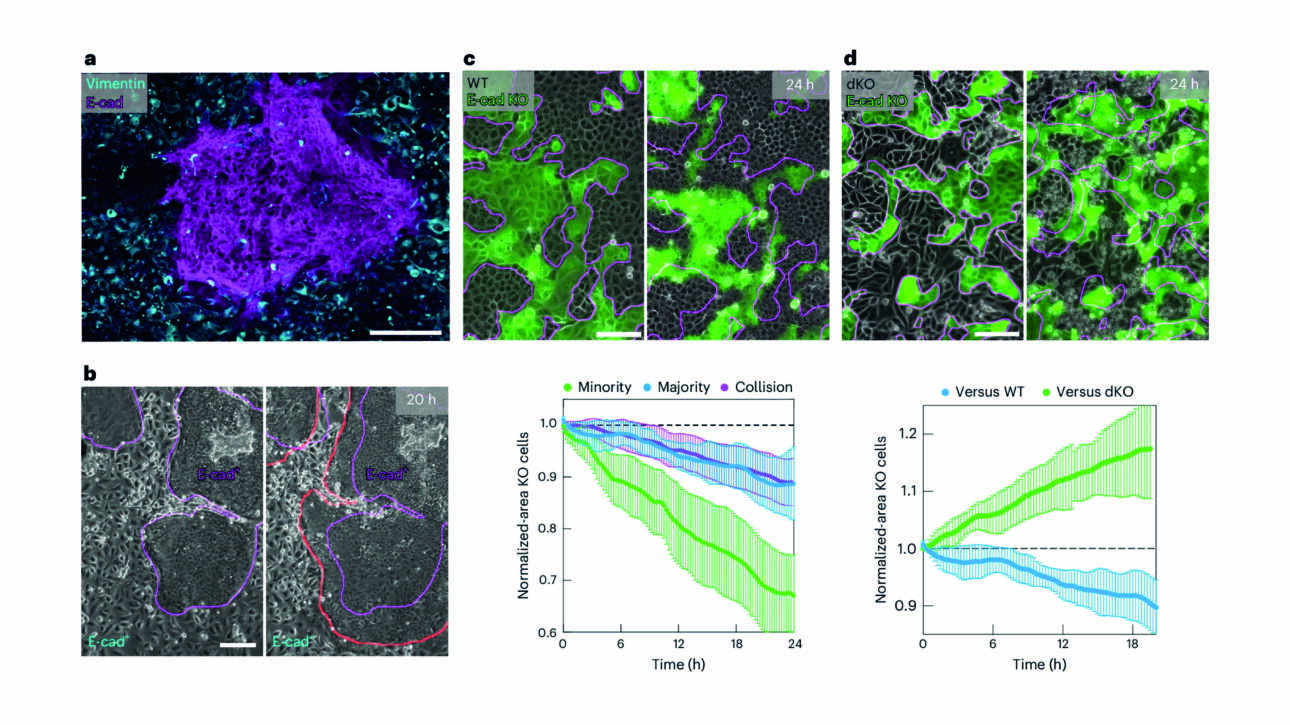
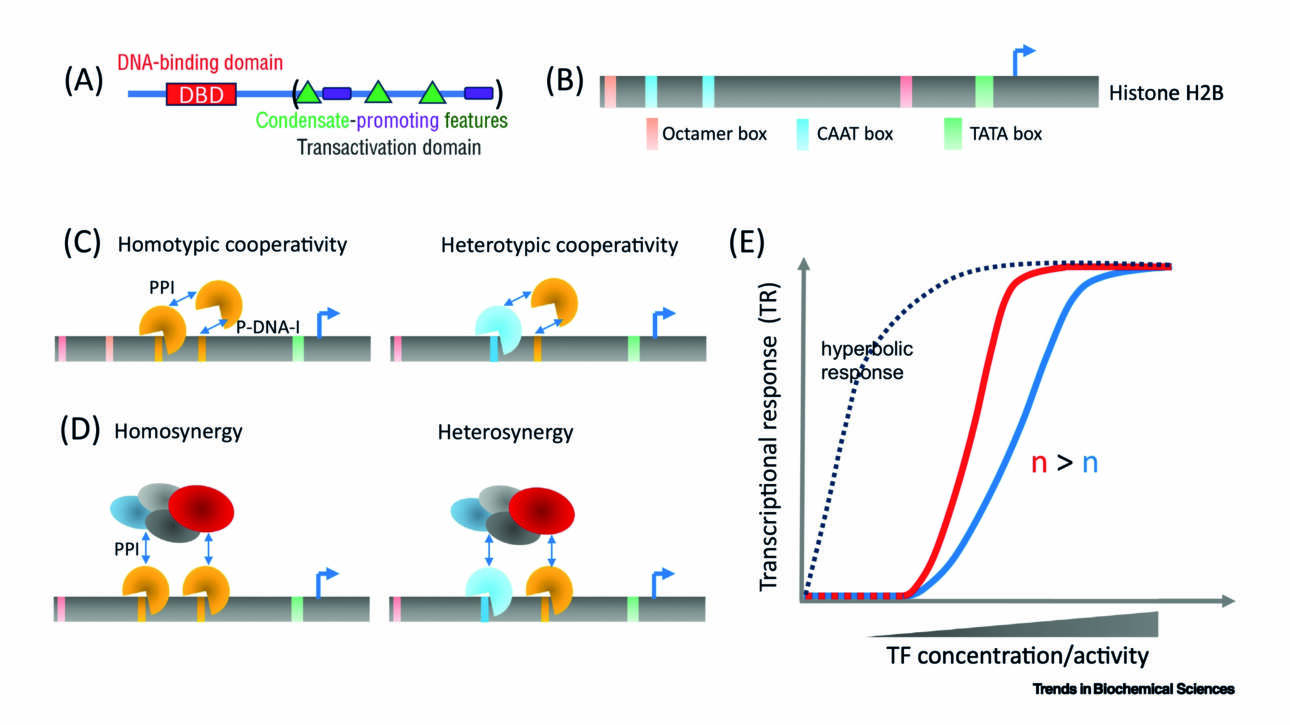
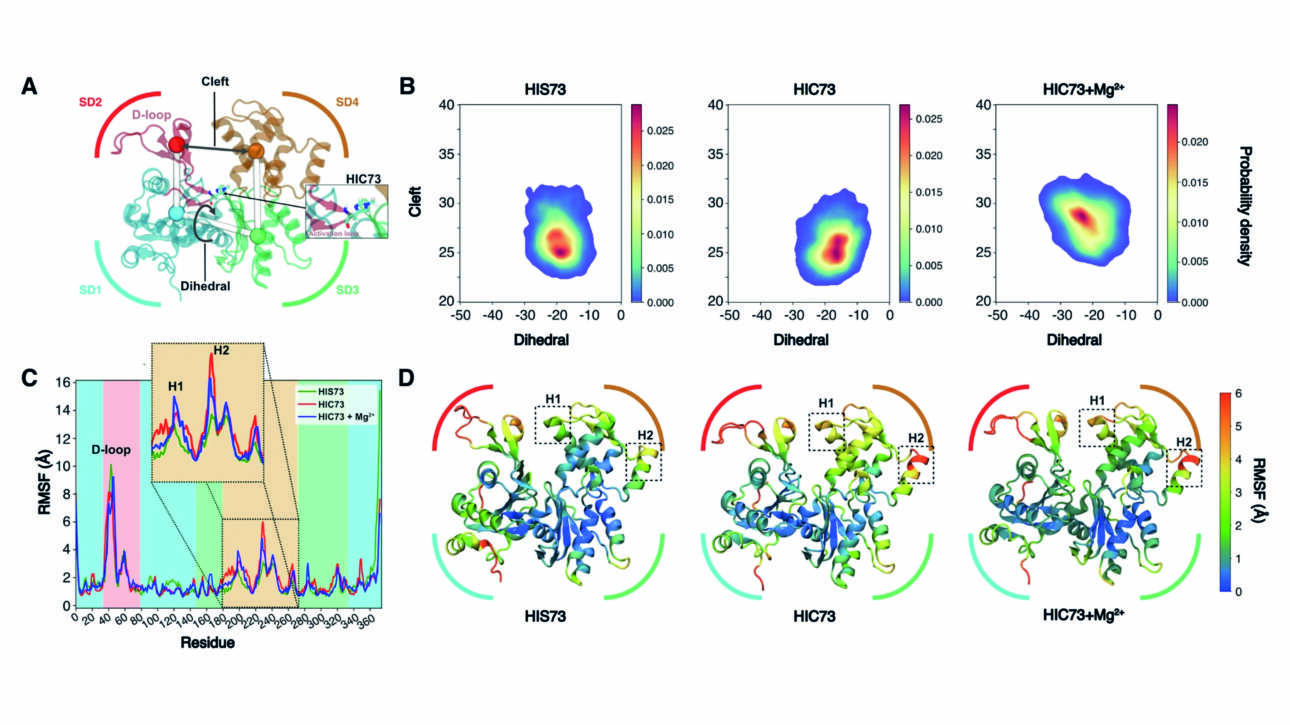
L'équipe Wassmann a publié un nouvel article dans Current Biology :
Prolonged metaphase II arrest weakens Aurora B/C-dependent error correction in mouse oocytes
Résumé :
Segregation errors in meiosis lead to aneuploid gametes and consequently to the development of trisomies, spontaneous abortion and fertility issues. Chromosome attachment to the microtubules of the bipolar spindle is a…