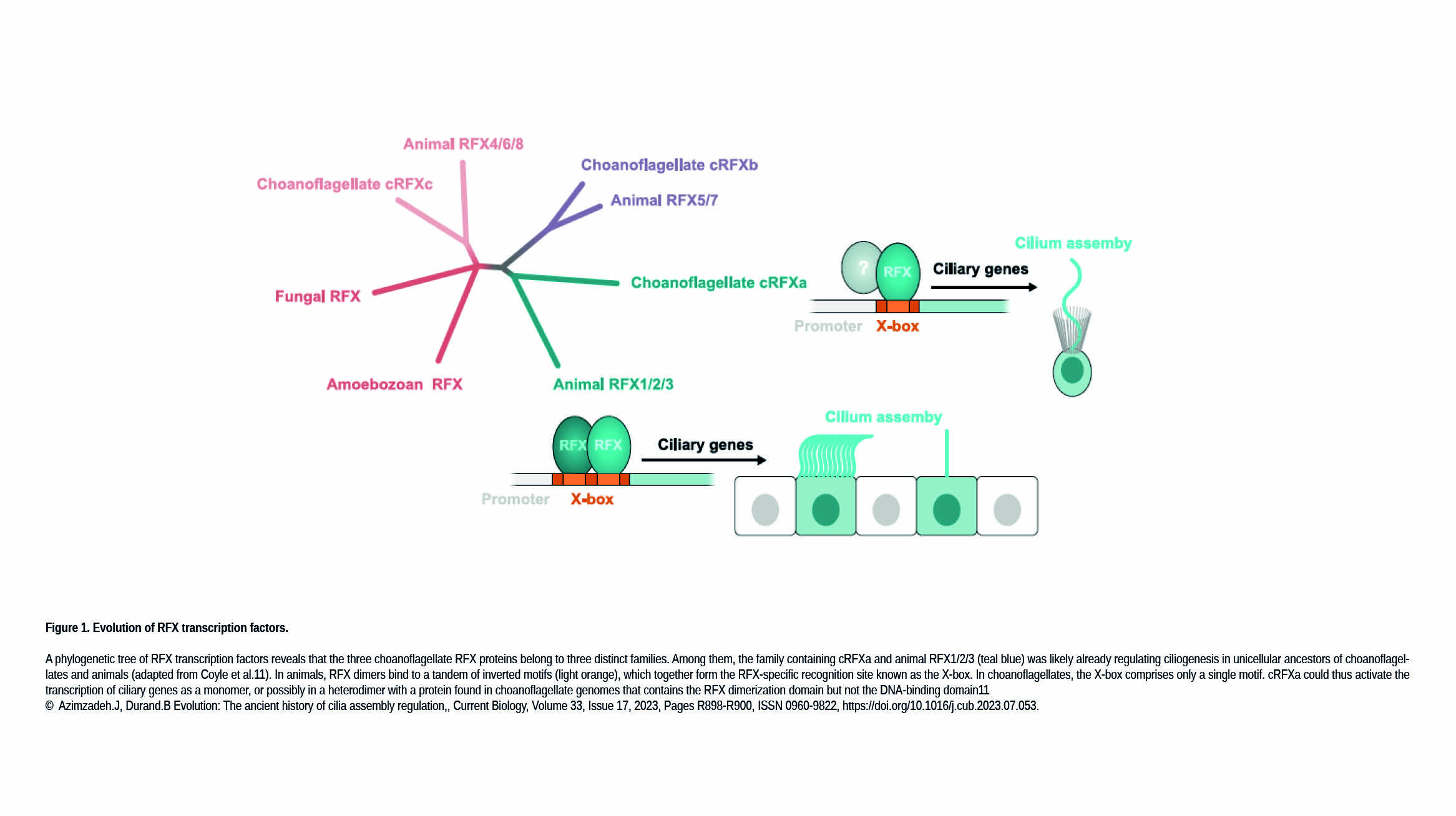
L'équipe Azimzadeh a récemment publié dans Current Biology :
Evolution: The ancient history of cilia assembly regulation
Résumé :
A new study identifies a conserved regulatory mechanism for cilia assembly in the closest unicellular relatives of animals, suggesting that this mechanism was already present in a common unicellular ancestor and was repurposed during the transition to multicellularity.